Ardoukôba Volcano
Updated: Apr 25, 2024 05:50 GMT -
Fissure vent(s), Pyroclastic cone(s), Tuff cone(s) 298 m / 978 ft
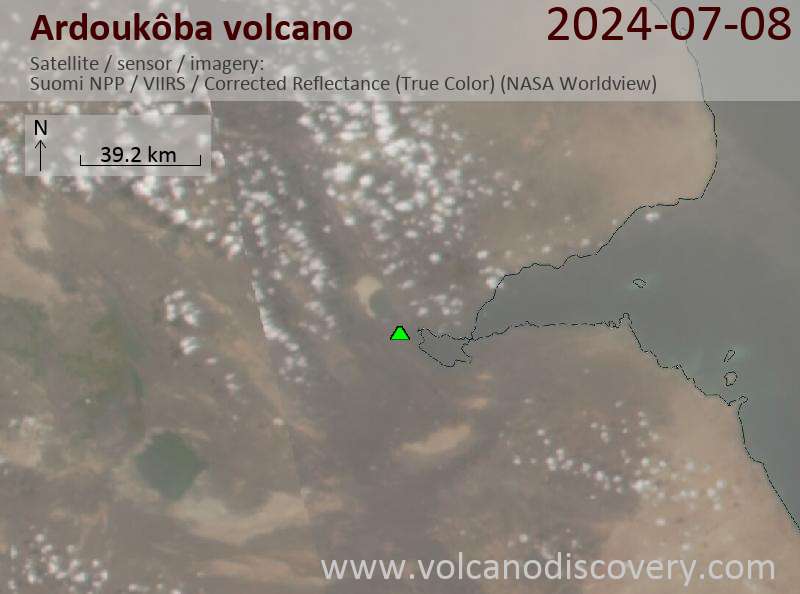
Djibouti, 11.58°N / 42.47°E
Current status: normal or dormant (1 out of 5)
Djibouti, 11.58°N / 42.47°E
Current status: normal or dormant (1 out of 5)
The Ardoukôba (Asal) Rift in Djibouti, trending NW from the Red Sea, contains a broad area of youthful fissure vents between Lake Asal and the Ghoubbat al Kharab gulf. It is subaerially exposed over 12 km between these two bodies of water and contains numerous basaltic cinder and spatter cones.
[smaller] [larger]
Ardoukôba volcano eruptions: 1978
Latest nearby earthquakes
| Time | Mag. / Depth | Distance / Location | |||
Background
The silicic centers of Eger Alayta and Asa Aleyta, on the N and S sides, are remnants of a Pleistocene silicic center that has been disrupted and spread apart. Magma-water interaction has produced tuff cones, some of which form islands or are breached by the sea. The most recent lava flows are younger than lake sediments deposited 5,300 years ago. These lavas were thought to have been erupted during the past 3,000 years (Delibrias et al., 1975). The fissure erupted in 1978, producing a small cinder cone and lava flows that covered part of the rift floor near the Red Sea.Source: Smithsonian / GVP