Aucanquilcha Volcano
Northern Chile, Bolivia and Argentina (South America), -21.22°S / -68.47°W
Current status: normal or dormant (1 out of 5)
Aucanquilcha is a massive stratovolcano in the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes in northern Chile. Volcán Aucanquilcha (also known as Cerro Aucancquilche) is the youngest of about 20 volcanoes and cones that form the Aucanquilcha Volcanic Cluster and one the largest volcanoes of northern Chile.
The world's highest permanent human settlement was located below a sulfur mine in the summit region of Cerro Aucanquilcha at an elevation of 5500 m. The mine was operated between 1913 and 1990's. The volcano also has one of the world's highest roads reaching 5900 m altitude.
Aucanquilcha The youngest lava flows of the volcano are younger than 10,000 years, and overlie glacial morains on the upper southern flanks. At present, there is fumarolic activity at the volcano.
Aucanquilcha volcano eruptions: younger than 10,000 years, 780,000 - 400,000 years ago
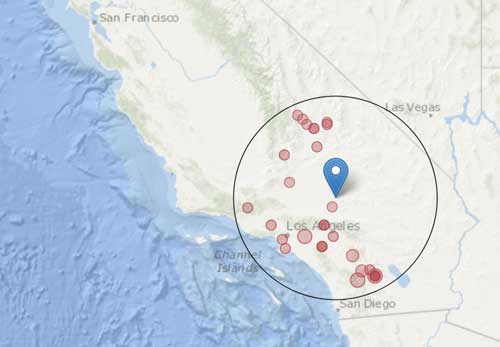
Latest nearby earthquakes
| Time | Mag. / Depth | Distance / Location | |||
| Apr 24, 02:55 pm (La Paz) | 2.7 160 km | Info | |||
| Tuesday, April 23, 2024 GMT (2 quakes) | |||||
| Apr 23, 09:34 am (Santiago) | 2.8 121 km | Info | |||
| Apr 23, 03:09 am (Santiago) | 3.4 134 km | 12 km (7.2 mi) to the N | Info | ||
| Monday, April 22, 2024 GMT (1 quake) | |||||
| Apr 22, 08:57 am (Santiago) | 2.7 137 km | Info | |||
| Wednesday, April 17, 2024 GMT (1 quake) | |||||
| Apr 17, 02:06 am (Santiago) | 2.7 120 km | Info | |||
| Monday, April 15, 2024 GMT (1 quake) | |||||
| Apr 15, 01:40 pm (Santiago) | 3.0 122 km | 23 km (14 mi) to the W | Info | ||
Background
The Aucanquilcha Volcanic Cluster (AVC) has had persistent mostly effusive volcanic activity over the last 11+million years erupting a total volume of 327 ± 20 km3 lava.Aucanquilcha volcano proper is the youngest member of the AVC. It rises about 1,400 m from the surrounding terrain and has a volume of 45 km3 of dacite lava that were erupted during effusive eruptions over the past 1 million years, but most of this volume was erupted in the first 200,000 years, while little volume of lava was added in the paswt 800,000 years.
The volcano's broad summit area is an 8-km E-W ridge with at least 7 vents, and includes 4 peaks raching more than 6,000 meters. The alignment of vents is nearly perpendicular to the axis of the volcanic belt.
Lava has been erupted from a both the vents along the ridge as well as from lower flank vents at 5,600 and 5,900 m. Aucanquilcha's lava flows are mostly dacite in composition and rarely exceed 3 km length.
There are 2 small domes on the northwestern flank. A debris avalanche deposit occurs on the eastern side and a large dome-collapse driven pyroclastic flow deposit occurs on the western side of the volcano.
Sources:
- Global Volcanism Program
- Erik W. Klemetti und Anita L. Grunder (2008) "Volcanic evolution of Volcán Aucanquilcha: a long-lived dacite volcano in the Central Andes of northern Chile" BULLETIN OF VOLCANOLOGY, Volume 70, Number 5, pp 633-650
- Grunder et al (2006) "Eleven million years of arc volcanism at the Aucanquilcha Volcanic Cluster, northern Chilean Andes: implications for the life span and emplacement of plutons", Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, v 97, pp 415-436