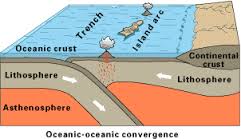
Chaîne des Puys Volcano
Updated: Jul 6, 2025 08:11 GMT -
Lava dome(s), Pyroclastic cone(s), Maar(s)
Massif Central, France, 45.78°N / 2.97°E 
Summit height: 1464 m / 4802 ft
Current status: normal or dormant (1 out of 5)
The Chaîne des Puys in the Massif Central of southern France is one of Europe's youngest volcanic fields. It consists of numerous cinder cones and maars roughly arranged on a N-S trending line. The last activity occurred only about 6000 years ago, which is why the volcanoes should be considered still active although there are no signs at present of any new activity to be expected in any near future.
[smaller] [larger]
Chaîne des Puys volcano eruptions: approx. 6000 years ago near Besse-en-Chandesse
Latest nearby earthquakes
| Date and Time | Mag / Depth | Distance / Location | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jul 4, 10:40 pm (Universal Time) | 0.9 0 km | 24 km (15 mi) to the N | Info | ||
| Jul 4, 10:39 pm (Universal Time) | 1.3 5.6 km | 25 km (15 mi) to the N | Info | ||
| Thursday, July 3, 2025 GMT (1 quake) | |||||
| Jul 3, 04:31 am (Universal Time) | 0.9 6 km | 21 km (13 mi) to the S | Info | ||
| Wednesday, July 2, 2025 GMT (1 quake) | |||||
| Jul 2, 11:22 pm (Universal Time) | 1.2 15 km | 19 km (12 mi) to the N | Info | ||
| Tuesday, July 1, 2025 GMT (1 quake) | |||||
| Jul 1, 08:34 am (Universal Time) | 1.4 0 km | 30 km (19 mi) to the N | Info | ||
| Wednesday, June 25, 2025 GMT (1 quake) | |||||
| Jun 25, 07:57 am (Universal Time) | 1.1 0 km | 26 km (16 mi) to the SE | Info | ||
| Tuesday, June 24, 2025 GMT (1 quake) | |||||
| Jun 24, 06:50 pm (Universal Time) | 0.8 0 km | 23 km (14 mi) to the S | Info | ||
Background
The Chaîne des Puys form a N-S-trending chain of basaltic and trachytic cinder cones, basaltic maars, and trachytic lava domes in France's Massif Central that has been active into the Holocene.Construction of the present-day Chaîne des Puys began about 70,000 years before present (BP), and was largely completed by the beginning of the Holocene. Holocene eruptions constructed lava domes such as the Puy de Dôme, whose growth was accompanied by pyroclastic flows, cinder cones that fed lengthy lava flows, and maars. The latest well-documented activity took place about 6000 BP near Besse-en-Chandesse and included the powerful explosions that formed the Lac Pavin maar.
The dating of younger tephras has not yet been confirmed, and reports of historical eruptions as late as 1000 BP have been discredited.
Significant volcanic eruptions: Chaîne des Puys volcano
No historic eruptions are known from Chaîne des Puys volcano, but evidence from at least 8 eruptions during the past 10,000 years can be found in the geological record.
The table below lists all known eruptions (date in bold face) of Chaîne des Puys volcano in historic times and during the past 10,000 years. Updates on the most recent volcanic activity of Chaîne des Puys can be found on the news page of Chaîne des Puys volcano.
| Date | Note | VEI | Deaths | Damage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Montcineyre, Estivadoux, Pavin | ? | ||||
| Puy de Come, Puy Montchier | ? | ||||
| Puy de Lassolas, Puy de la Vache | ? | ||||
| Puy de Pariou | ? | ||||
| Puys Chopine, Vasset, Cratère Kilian | ? | ||||
| ? | |||||
| Puy Mey | ? | ||||
| Western Puy de Dôme | ? | ||||
Remark:
Our list of volcanic eruptions closely follows the database of eruptions of the Smithsonian's Global Volcanism Project (GVP), the internationally most recognized data source for volcanic eruptions, but also includes significant eruptive episodes or related volcano events. "Volcanic eruptions" are usually to be understood as sequences of individual eruptive episodes that can follow each other, or even overlap (if several vents are involved), and can last many years, decades or even longer. For example, the current activity of Stromboli volcano is understood as a single eruption that has been ongoing since 1934.
Sources: NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI), Global Significant Volcanic Eruptions Database. doi:10.7289/V5TD9V7K | Global Volcanism Project / Smithsonian Institution
Chaîne des Puys Volcano FAQ
+When was the last eruption of Chaîne des Puys volcano?
The last confirmed eruption of Chaîne des Puys occurred around 4040 BC.
Latest satellite images
Chaîne des Puys Volcano Maps
Below is a selection of maps showing the location and surroundings of the volcano at various resolutions based on aerial-imagery / terrain maps. Feel free to use them for non-commercial purposes on your blog or website as long as you credit them with a link back to this page (click to copy it).
Satellite/aerial-type map of Chaîne des Puys volcano (world scale)
Terrain-type map of Chaîne des Puys volcano (world scale)
Satellite/aerial-type map of Chaîne des Puys volcano (region scale large)
Terrain-type map of Chaîne des Puys volcano (region scale large)
Satellite/aerial-type map of Chaîne des Puys volcano (region scale medium)
Terrain-type map of Chaîne des Puys volcano (region scale medium)
Satellite/aerial-type map of Chaîne des Puys volcano (region scale small)
Terrain-type map of Chaîne des Puys volcano (region scale small)
Satellite/aerial-type map of Chaîne des Puys volcano (local scale large)
Terrain-type map of Chaîne des Puys volcano (local scale large)
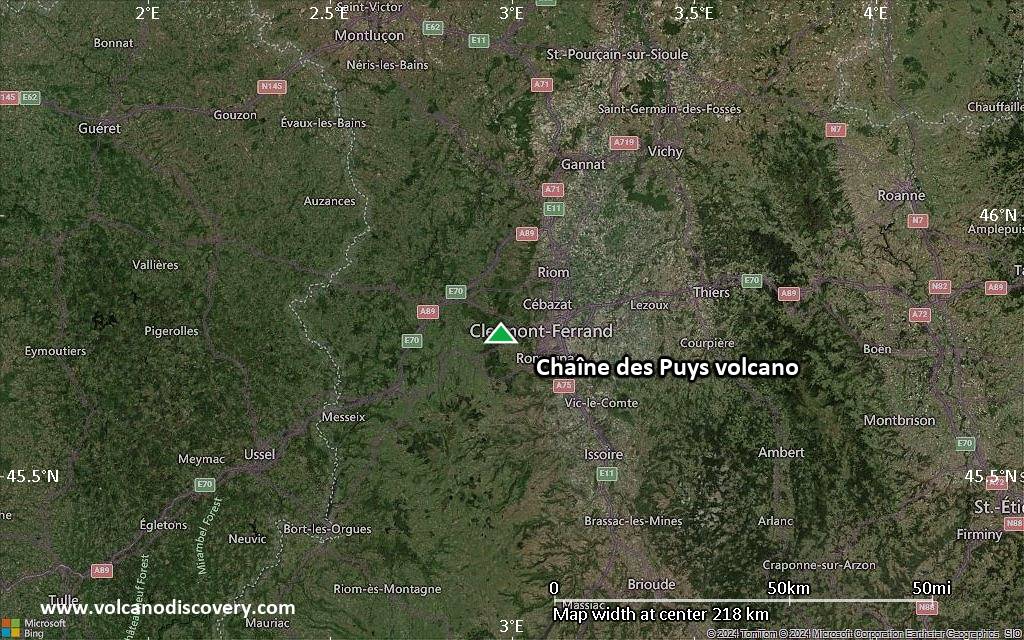
Satellite/aerial-type map of Chaîne des Puys volcano (local scale medium)
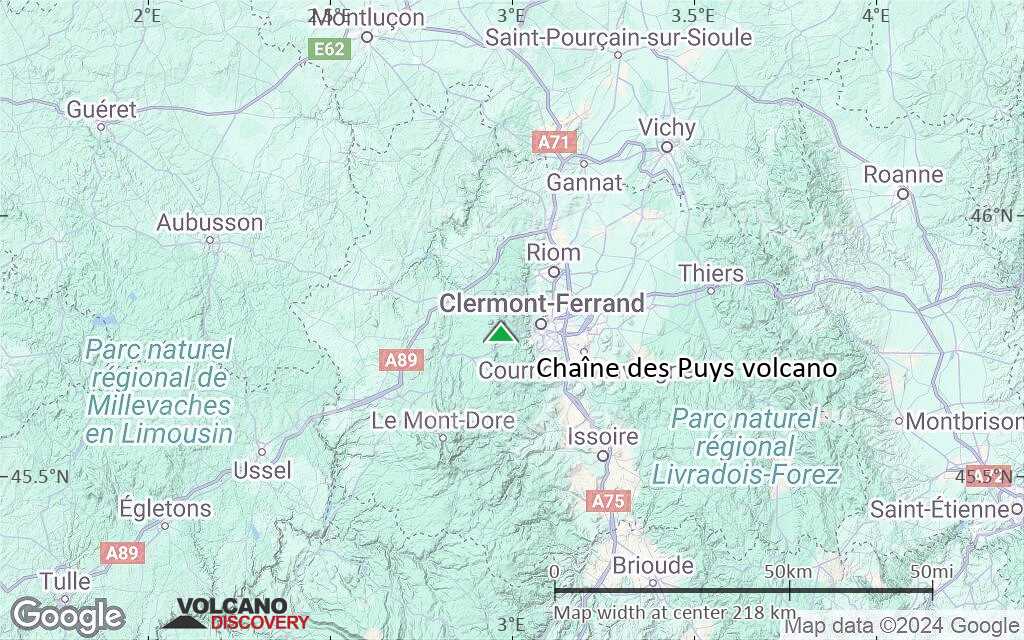
Terrain-type map of Chaîne des Puys volcano (local scale medium)
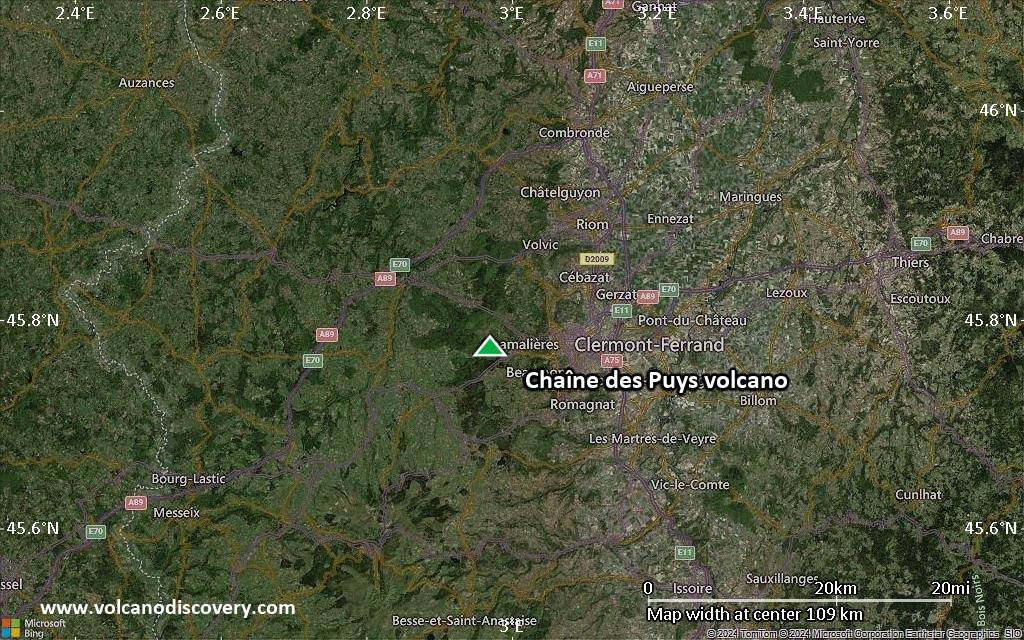
Satellite/aerial-type map of Chaîne des Puys volcano (local scale small)
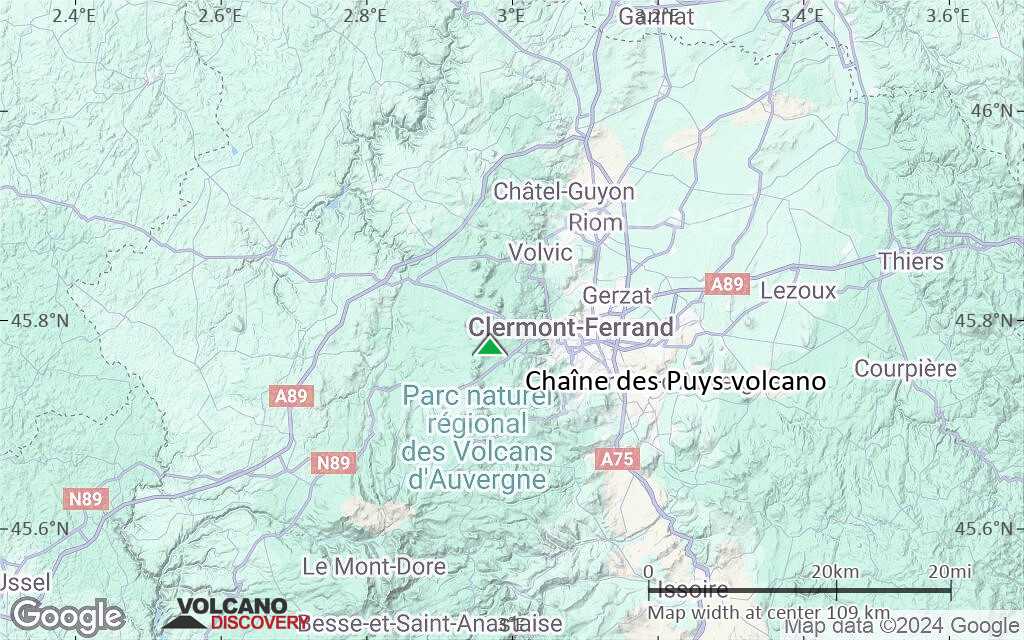
Terrain-type map of Chaîne des Puys volcano (local scale small)
Satellite/aerial-type map of Chaîne des Puys volcano (scale of 10s of km)
Terrain-type map of Chaîne des Puys volcano (scale of 10s of km)
Satellite/aerial-type map of Chaîne des Puys volcano (scale of 20-40 km)
Terrain-type map of Chaîne des Puys volcano (scale of 20-40 km)
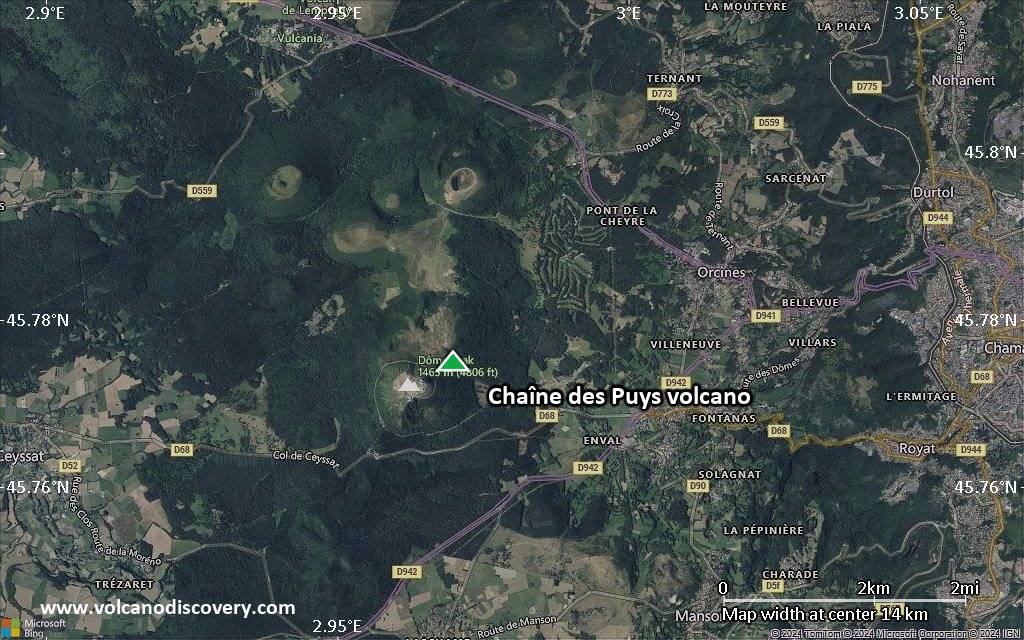
Satellite/aerial-type map of Chaîne des Puys volcano (scale of approx. 10-20 km)
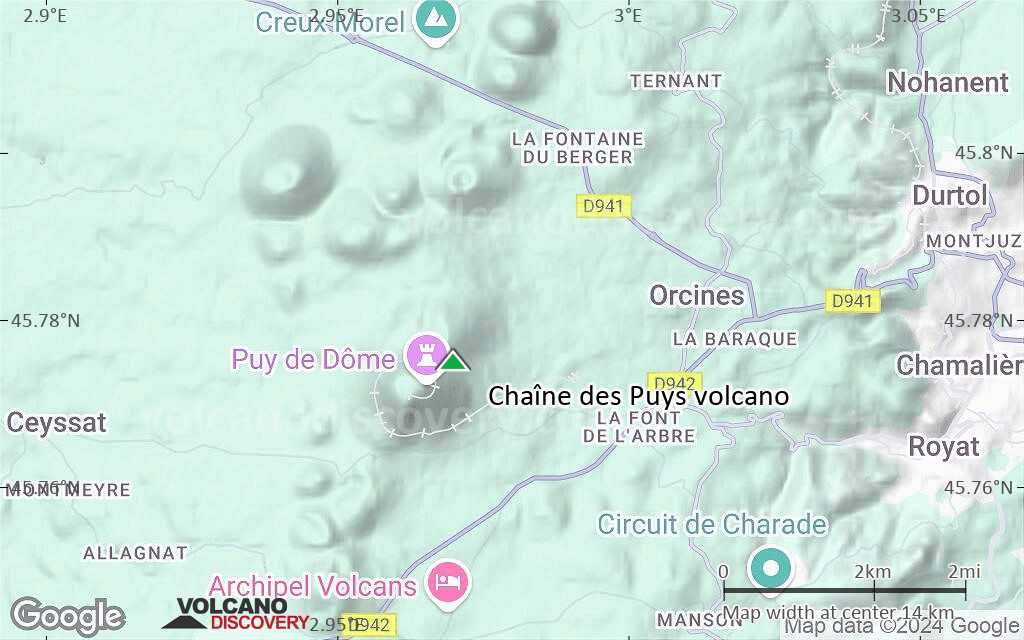
Terrain-type map of Chaîne des Puys volcano (scale of approx. 10-20 km)
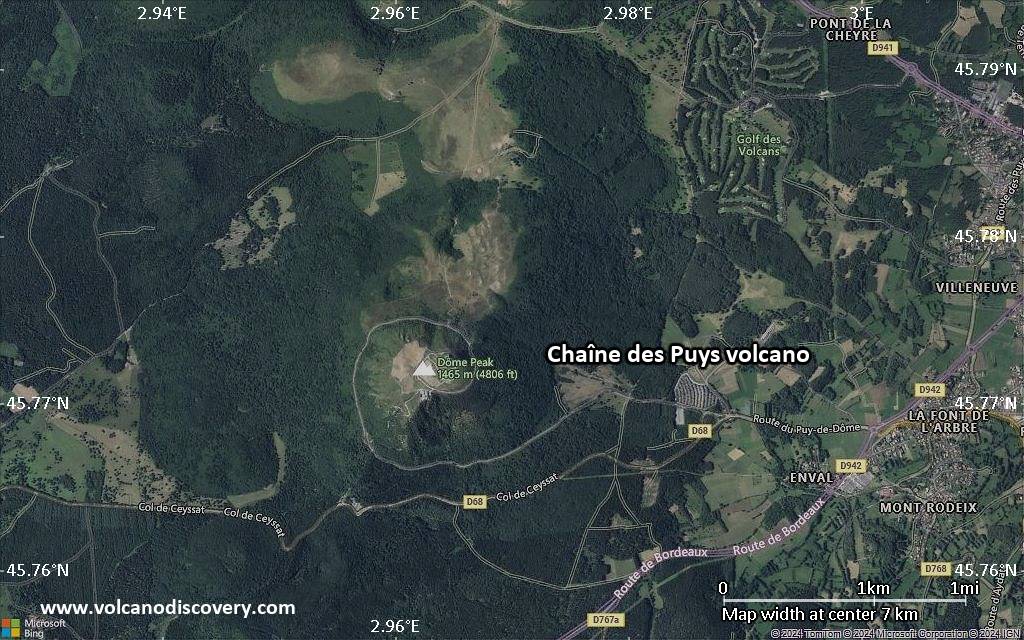
Satellite/aerial-type map of Chaîne des Puys volcano (scale of 5-10 km)
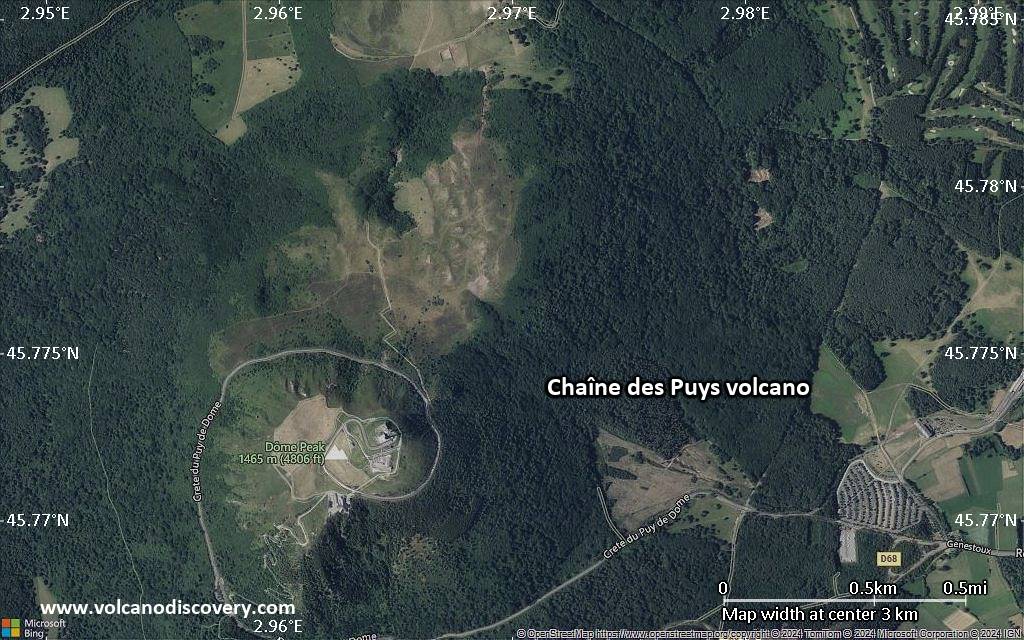
Satellite/aerial-type map of Chaîne des Puys volcano (scale of few kilometers)