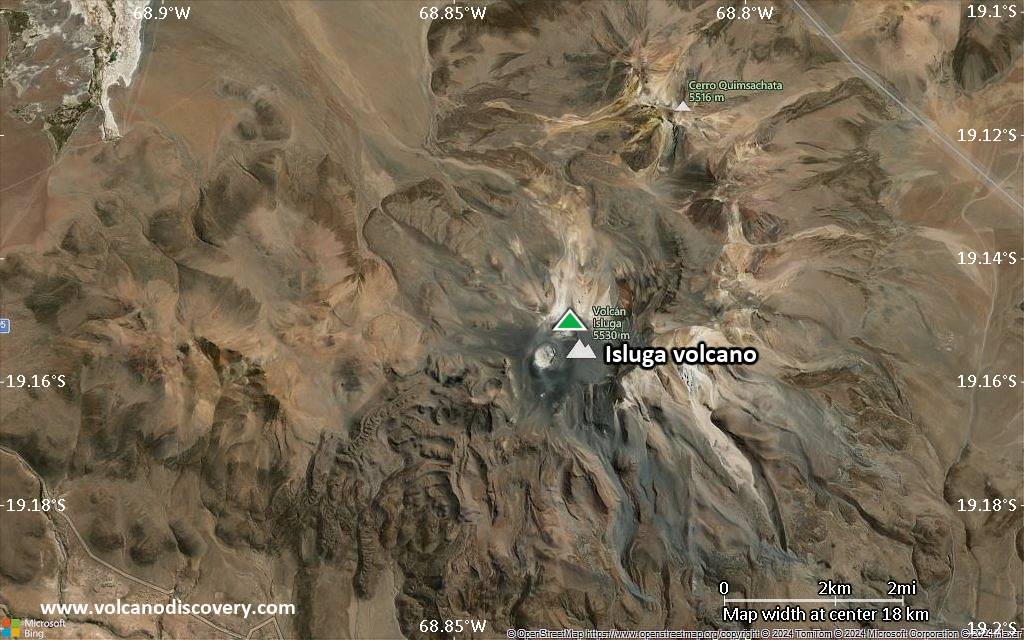
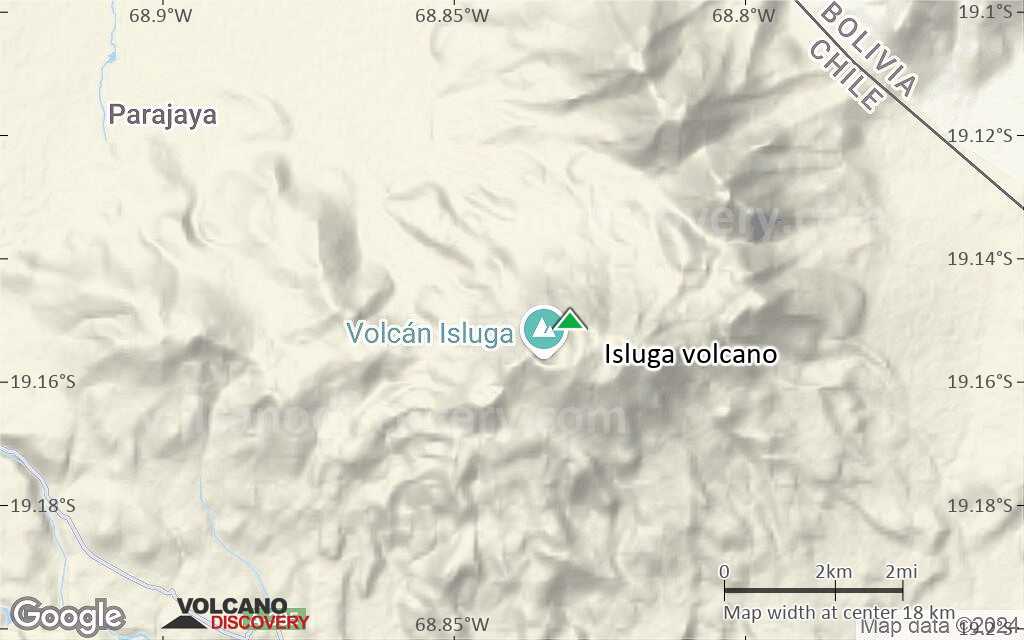
Isluga Volcano
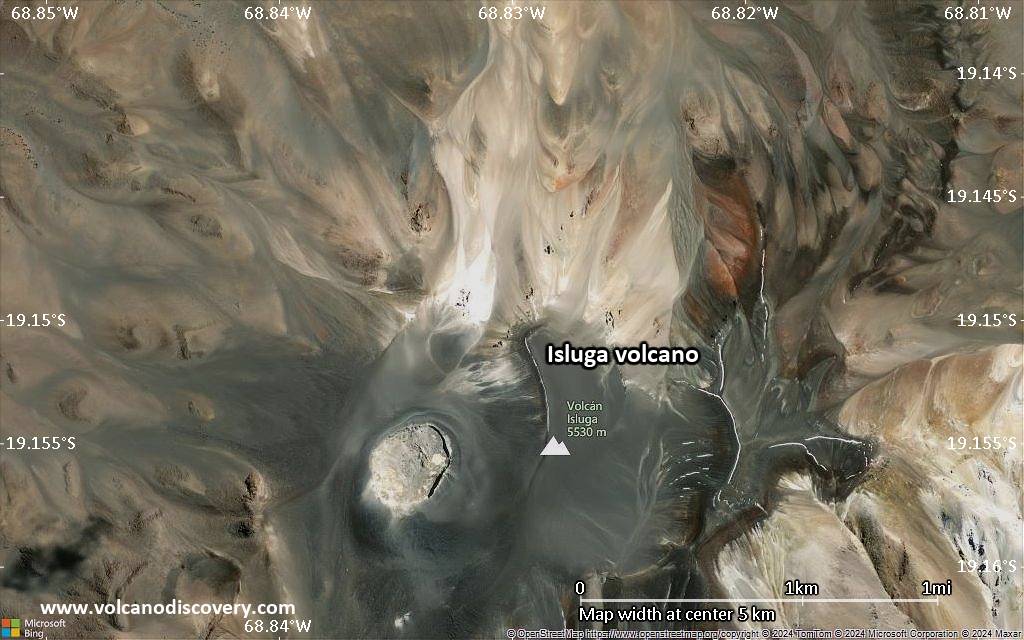
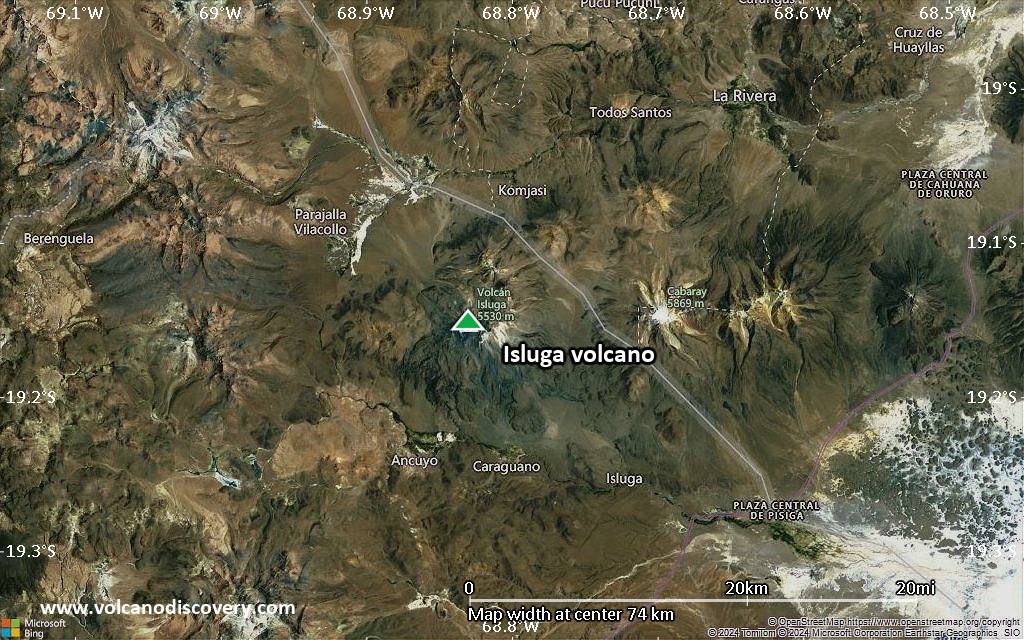
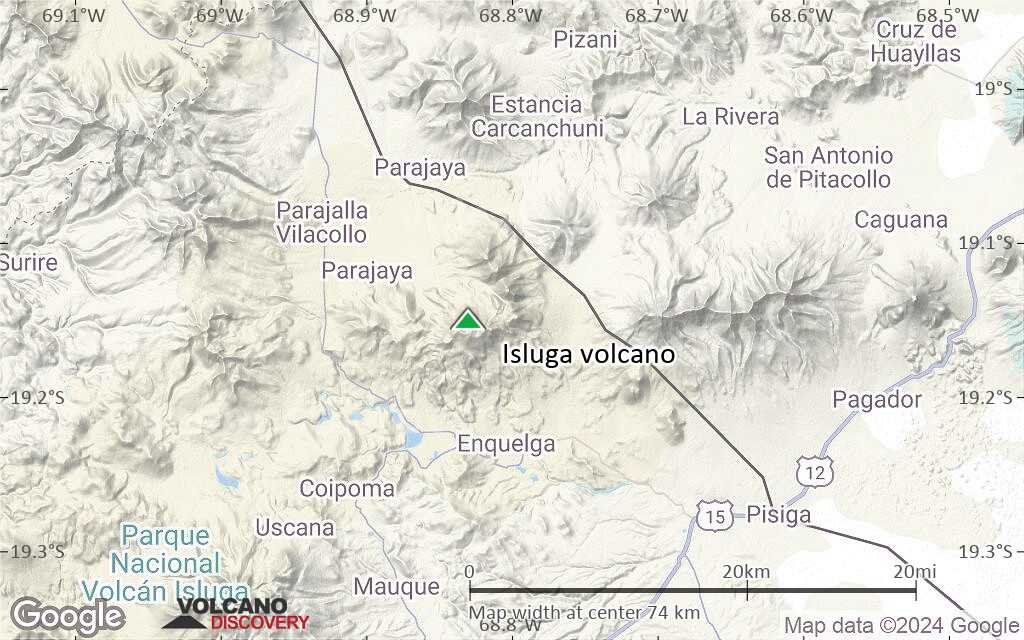
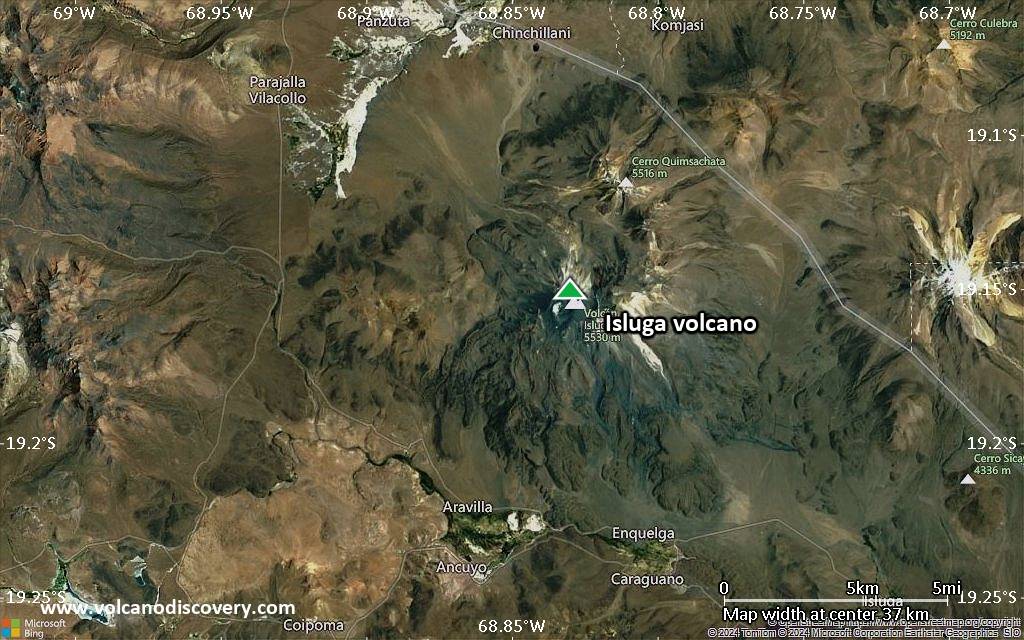
Volcán Isluga volcano is a broad stratovolcano in northern Chile 7 km west of the Bolivian border and forms the western end of a group of volcanoes extending to Tata Sabaya volcano in Bolivia. Isluga volcano is part of the 175,000 hectares Isluga National Park.
Isluga's summit contains a morphologically young, 400 m wide crater at the western end of the elongated, snow-covered summit region. Many lava flows with distinct levees can be seen on the southern flank and in 1878, lava flows destroyed several towns. At present, there is fumarolic activity at Isluga volcano, the last confirmed eruption was a small explosive eruption in 1913.
Isluga volcano eruptions: 1960(?), 1913(?), 1885, 1878, 1877, 1869, 1868, 1863
Latest nearby earthquakes
| Date and Time | Mag / Depth | Distance / Location | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Background
Recent eruptions were phreatomagmatic and produced surges whose deposits can be found around the active crater. Holocene lava flows cover the northernmost ridge of the volcano.An older glaciated dacite flow from the northwest side of the volcano has been dated at at 96,000 years. Lavas from Isluga overlie rocks from a dissected volcano (Quimsachatas) to the north and northeast, which erupted 566,000 years ago.
(From: Wörner et al (2000), "Geochronology (40Ar/39Ar, K-Ar and He-exposure ages) of Cenozoic magmatic rocks from Northern Chile (18-22°S): implications for magmatism and tectonic evolution of the central Andes", Rev. geol. Chile vol.27 n.2
Eruptions of Isluga volcano
Major eruptions occurred in 1868, 1869, 1877, and 1878, and smaller eruptions in 1863, 1885 and 1913. The activity reported in 1960 is uncertain.
Significant volcanic eruptions: Isluga volcano
| Date | Note | VEI | Deaths | Damage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
?? | Uncertain Eruption | 2? | |||
Historical obs./docs. | 2 | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | 1? | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | 2 | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | 2? | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | 2 | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | 2? | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | 1? | ||||
Isluga Volcano FAQ
+When was the last eruption of Isluga volcano?
The last confirmed eruption of Isluga occurred in 1913.
+How often does Isluga volcano erupt?
Since 1863, Isluga volcano has had at least 7 historically documented eruptions. This means that it erupts on average every 23.1 years.
+How active is Isluga volcano at present?
Isluga volcano is occasionally active: Since 1900, it has had one eruption, which occurred in 1913.
+When was the largest eruption of Isluga volcano?
The largest eruption of Isluga volcano in historic times occurred in 1913. It ranks as a strombolian to vulcanian eruption with a magnitude 2 on the VEI (Volcanic Explosivity Index) scale.
Latest satellite images
Isluga Volcano Maps