Sacabaya Volcano
Updated: Apr 29, 2024 13:12 GMT -
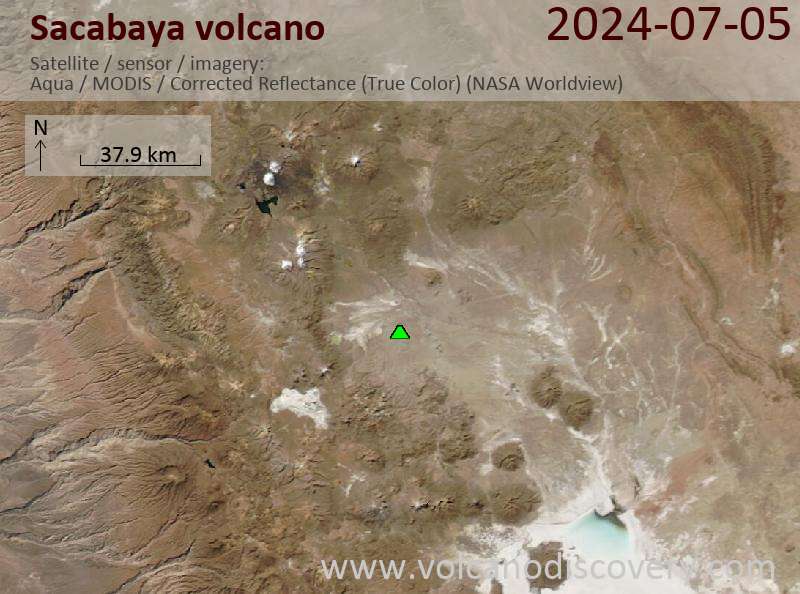
pyroclastic shield 4215 m / 13,829 feet
Northern Chile, Bolivia and Argentina (South America), -18.62°S / -68.75°W
Current status: normal or dormant (1 out of 5)
Northern Chile, Bolivia and Argentina (South America), -18.62°S / -68.75°W
Current status: normal or dormant (1 out of 5)
Last update: 4 Jun 2016
Volcán Sacabaya (also known as Tambo Quemado or Cerro Quemado) is a low pyroclastic shield near the Rio Lauca on the Bolivian Altiplano 26 km from the border with Chile.
It is not known when it last erupted, but its very fresh morphology suggests a young (Holocene) age and there is fumarolic activity.
[smaller] [larger]
Sacabaya volcano eruptions: probably within the past 10,000 years
Latest nearby earthquakes
| Time | Mag. / Depth | Distance / Location | |||
Background
from Smithsonian / GVP Tambo Quemado volcano information:Tambo Quemado consists of a broad ignimbrite shield capped by an elongated NNE-SSW-trending vent area about 2 x 3.5 km in diameter formed by 3 large overlapping craters. The youngest crater lies at the southern end of the 4215-m-high summit region and contains a blocky lava dome. Wind has redistributed tephra deposits to the east and south, forming sand dunes.