Ciomadul Volcano
Updated: Aug 28, 2025 01:32 GMT -
Lava dome(s)
Romania, 46.13°N / 25.88°E 
Summit height: 1289 m / 4229 ft
Current status: (probably) extinct (0 out of 5)
Last update: 22 Feb 2020
The Ciomadul is the youngest volcano of the Carpathian-Pannonian region. Its most recent activity dates back a few tens of thousands years and produced abundant pyroclastic fall and flow deposits. The volcano consists of a complex of lava domes in the Calimani-Harghita Range.
[smaller] [larger]
Ciomadul volcano eruptions: between 32,600 and 27,500 years ago
Latest nearby earthquakes
| Date and Time | Mag / Depth | Distance / Location | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Background
The Ciomadul lava-dome complex is the youngest volcanic center of the Carpathian-Pannonian region. Located at the SE end of the Calimani-Harghita Range, it consists of a dacitic dome complex formed about 500-700 ka.The dome complex is cut by twin craters, Mohos and St. Anna. The latest eruption, from St. Anna, produced subplinian airfall and pyroclastic-surge deposits that have been variously dated between about 10.7 and 42 ka. Pecskay et al. (2006) noted ages of 1.0-0.03 Ma. A number of samples from other South Harghita locations (Porcuhu, Cucu, Kapus, Pilisca, Balvanyos, Haramul Mare, and Koves Peak) had Quaternary dates.
Source: GVP
Cited reference:
Pecskay Z, Lexa J, Szakacs A, Seghedi I, Balogh K, Konecny V, Zelenka T, Kovacs M, Poka T, Fulop, Marton E, Panaiotu C, Cvetkovic V, 2006. Geochronology of Neogene magmatism in the Carpathian arc and intra-Carpathian area. Geologica Carpathica 57:6, p. 511-530.
Latest satellite images
Ciomadul Volcano Maps
Below is a selection of maps showing the location and surroundings of the volcano at various resolutions based on aerial-imagery / terrain maps. Feel free to use them for non-commercial purposes on your blog or website as long as you credit them with a link back to this page (click to copy it).
Satellite/aerial-type map of Ciomadul volcano (world scale)
Terrain-type map of Ciomadul volcano (world scale)

Satellite/aerial-type map of Ciomadul volcano (region scale large)
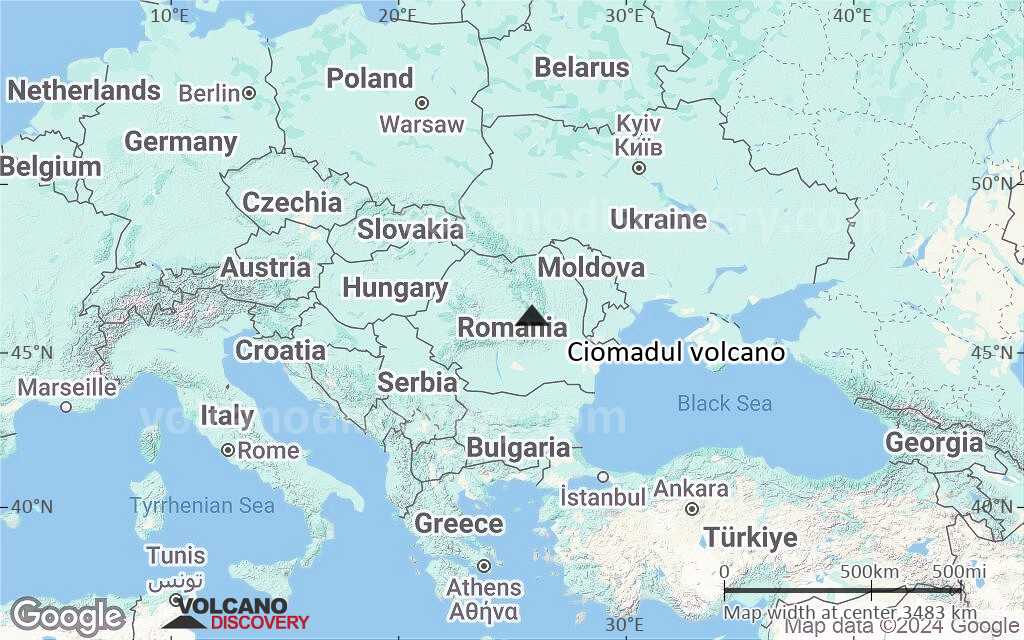
Terrain-type map of Ciomadul volcano (region scale large)

Satellite/aerial-type map of Ciomadul volcano (region scale medium)
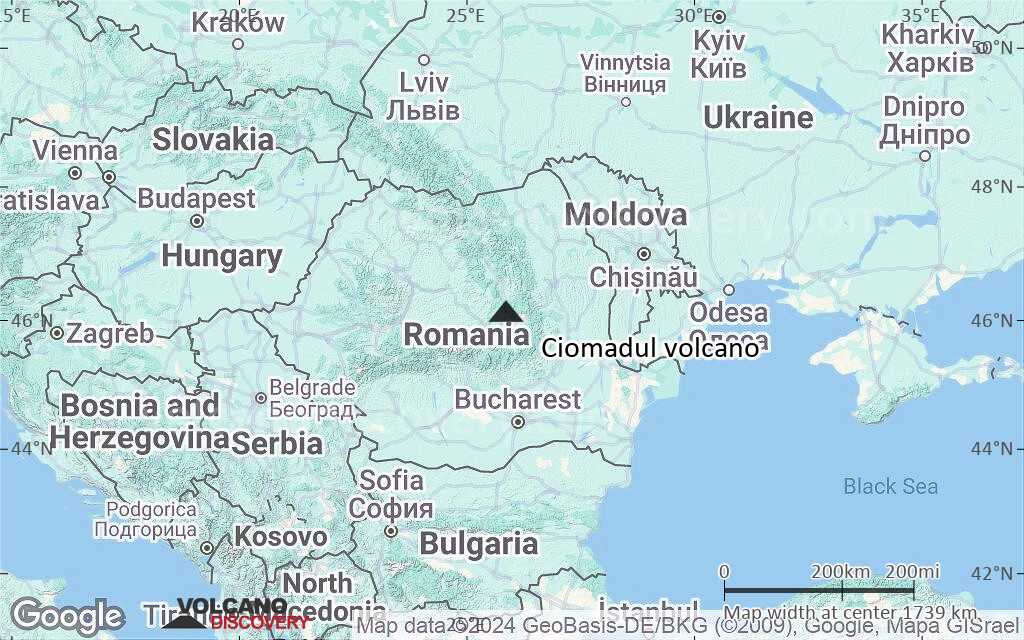
Terrain-type map of Ciomadul volcano (region scale medium)

Satellite/aerial-type map of Ciomadul volcano (region scale small)
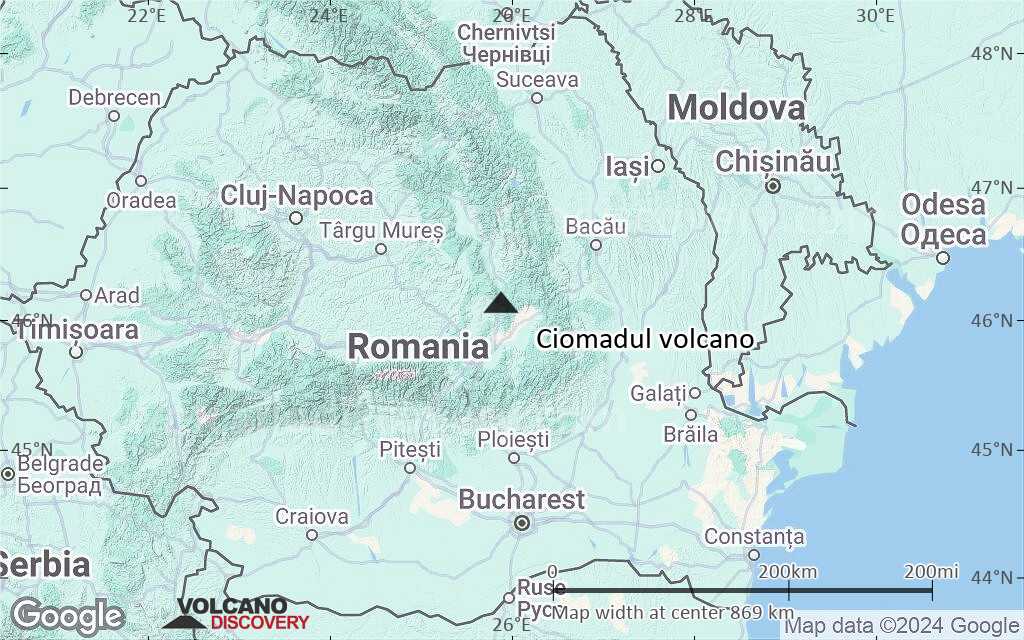
Terrain-type map of Ciomadul volcano (region scale small)

Satellite/aerial-type map of Ciomadul volcano (local scale large)

Terrain-type map of Ciomadul volcano (local scale large)
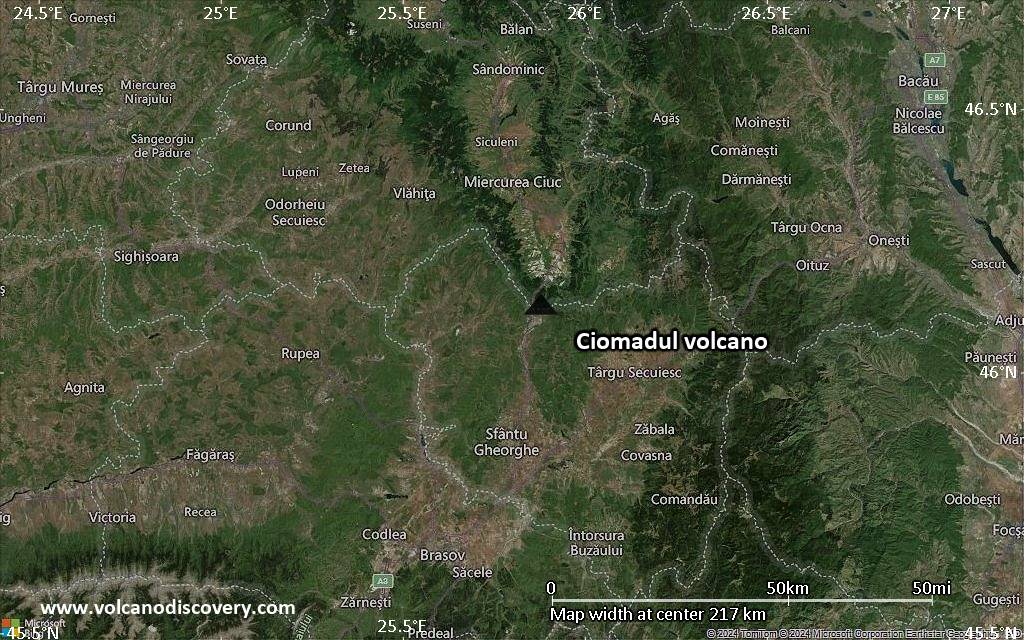
Satellite/aerial-type map of Ciomadul volcano (local scale medium)
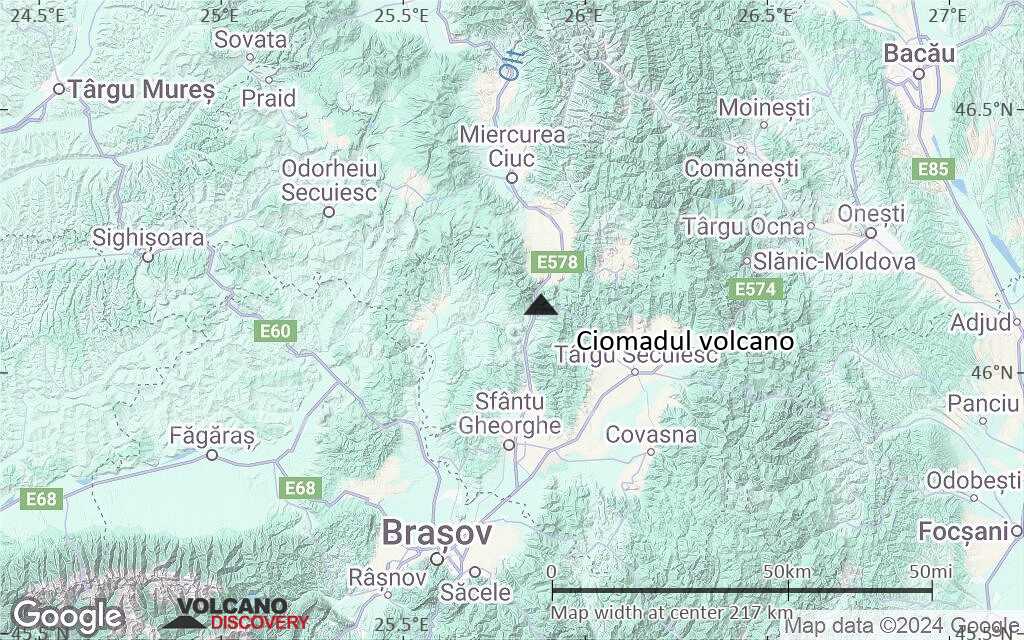
Terrain-type map of Ciomadul volcano (local scale medium)

Satellite/aerial-type map of Ciomadul volcano (local scale small)
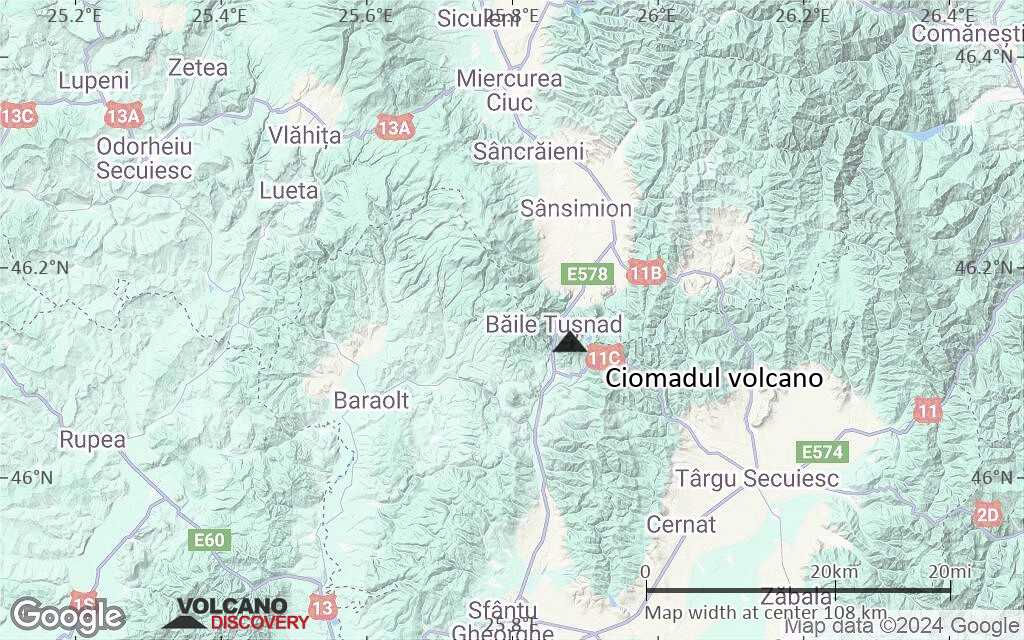
Terrain-type map of Ciomadul volcano (local scale small)
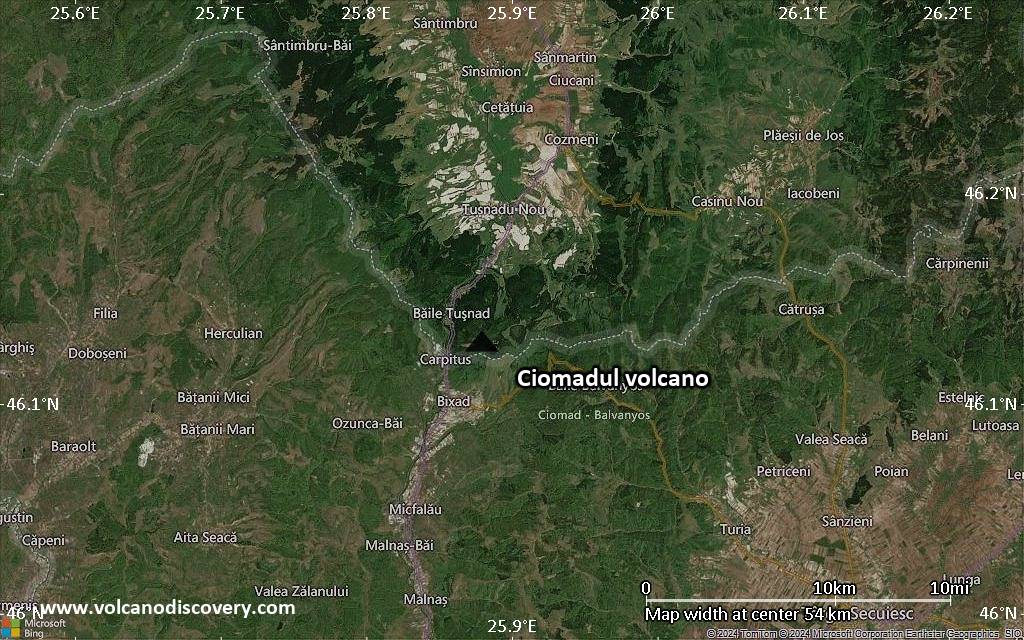
Satellite/aerial-type map of Ciomadul volcano (scale of 10s of km)

Terrain-type map of Ciomadul volcano (scale of 10s of km)
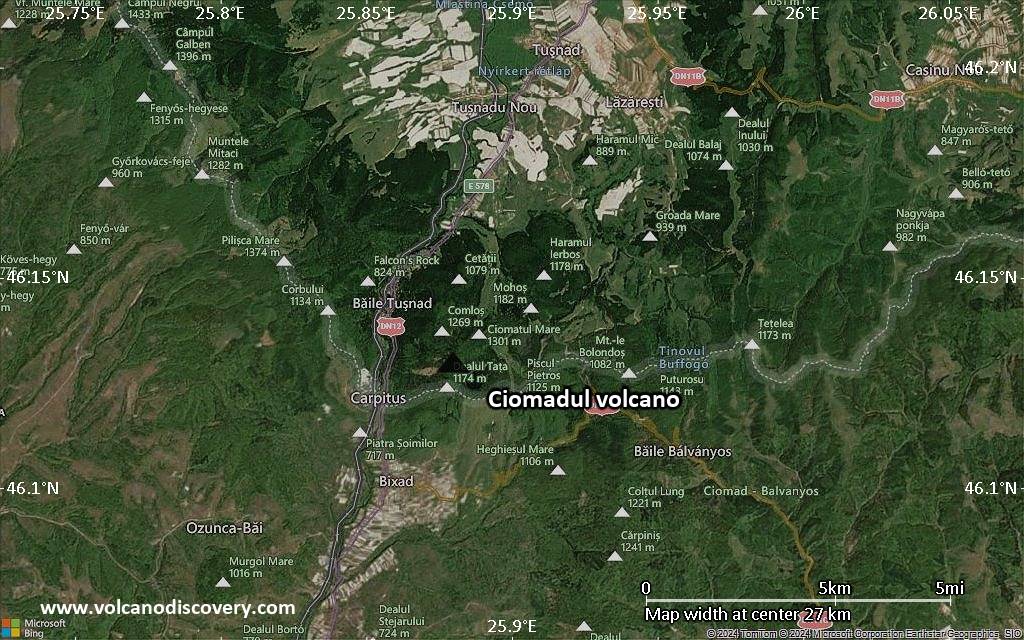
Satellite/aerial-type map of Ciomadul volcano (scale of 20-40 km)

Terrain-type map of Ciomadul volcano (scale of 20-40 km)

Satellite/aerial-type map of Ciomadul volcano (scale of approx. 10-20 km)
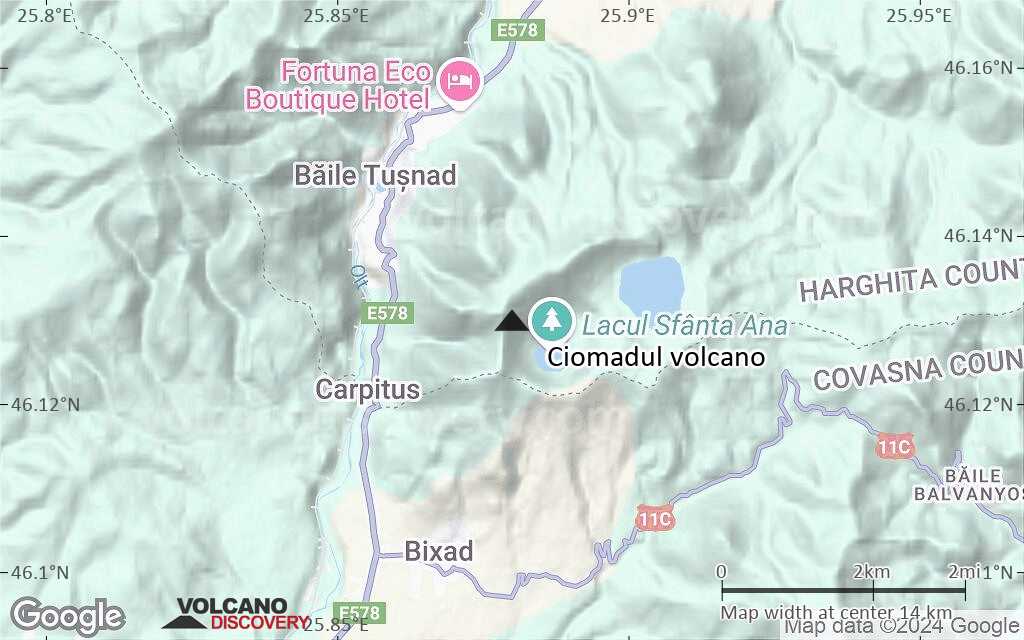
Terrain-type map of Ciomadul volcano (scale of approx. 10-20 km)

Satellite/aerial-type map of Ciomadul volcano (scale of 5-10 km)

Satellite/aerial-type map of Ciomadul volcano (scale of few kilometers)





















