Aguilera Volcano
Updated: Oct 10, 2025 00:17 GMT -
stratovolcano
Southern Chile and Argentina (South America), -50.33°S / -73.75°W 
Summit height: 2546 m / 8,353 ft
Current status: normal or dormant (1 out of 5)
Aguilera is a dacitic stratovolcano in the southernmost Chilean Andes and located west of Lake Argentina and NE of Peel Fjiord. Its geologic history is poorly known, but there Aguilera must have had a large explosive eruption less than about 3600 years ago, which left a prominent tephra layer.
Aguilera belongs to the Australandean Volcanic Zone of south Patagonia.
[smaller] [larger]
Aguilera volcano eruptions: 1250 BC ± 150 years
Latest nearby earthquakes
Background
Explosive eruption of Aguilera volcano 3600 years agoA large explosive eruption occurred at Aguilera volcano about 3600 years ago and is recognized by the "A1" tephra layer. The eruption was Plinian in size and erupted ca. 4-9 cubic km of magma. The A1 white tephra layer is deposited in thick sections along the shores of Lago Argentino. It is absent on Tierra del Fuego, but has a very wide distribution north of the Strait of Magellan. At 80 km distance, the airfall tephra layer is still over 10 cm thick and more than 5 cm thick in 130 km distance east of the volcano. This suggests that the wind was blowing from the SW at the time of the eruption and the plume drifted NE.
The pumice of the A1 tephra contains the mineral biotite as phenocrysts, which has not been found in other lavas of Aguilera.
Sources:
- Smithsonian / GVP Aguilera volcano information
- Charles R. Stern (2008) "Holocene tephrochronology record of large explosive eruptions in the southernmost Patagonian Andes", Bull. Volc., Volume 70, Number 4, pp. 435-454
Significant volcanic eruptions: Aguilera volcano
No historic eruptions are known from Aguilera volcano, but evidence from at least 2 eruptions during the past 10,000 years can be found in the geological record.
The table below lists all known eruptions (date in bold face) of Aguilera volcano in historic times and during the past 10,000 years. Updates on the most recent volcanic activity of Aguilera can be found on the news page of Aguilera volcano.
| Date | Note | VEI | Deaths | Damage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | |||||
| ? | |||||
Remark:
Our list of volcanic eruptions closely follows the database of eruptions of the Smithsonian's Global Volcanism Project (GVP), the internationally most recognized data source for volcanic eruptions, but also includes significant eruptive episodes or related volcano events. "Volcanic eruptions" are usually to be understood as sequences of individual eruptive episodes that can follow each other, or even overlap (if several vents are involved), and can last many years, decades or even longer. For example, the current activity of Stromboli volcano is understood as a single eruption that has been ongoing since 1934.
Sources: NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI), Global Significant Volcanic Eruptions Database. doi:10.7289/V5TD9V7K | Global Volcanism Project / Smithsonian Institution
Aguilera Volcano FAQ
+When was the last eruption of Aguilera volcano?
The last confirmed eruption of Aguilera occurred around 1253 BC.
+When was the largest eruption of Aguilera volcano?
The largest eruption known from the younger geological history of Aguilera volcano occurred around 1253 BC. It only has a VEI (Volcanic Explosivity Index) of , likely because it was a mainly effusive eruption generating lava flows but very little ash.
Latest satellite images
Aguilera Volcano Maps
Below is a selection of maps showing the location and surroundings of the volcano at various resolutions based on aerial-imagery / terrain maps. Feel free to use them for non-commercial purposes on your blog or website as long as you credit them with a link back to this page (click to copy it).

Satellite/aerial-type map of Aguilera volcano (world scale)
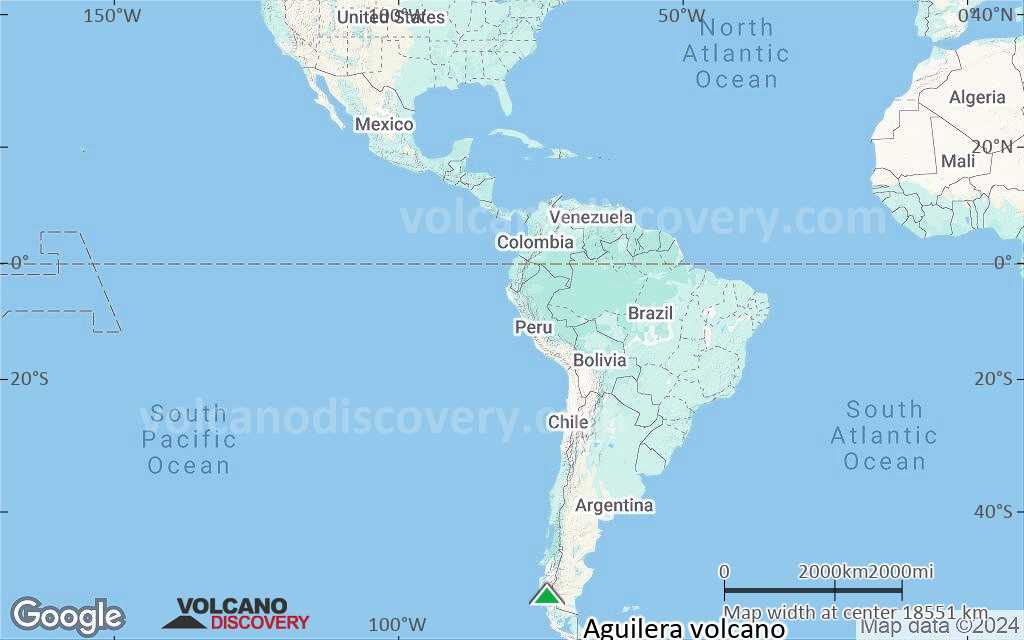
Terrain-type map of Aguilera volcano (world scale)
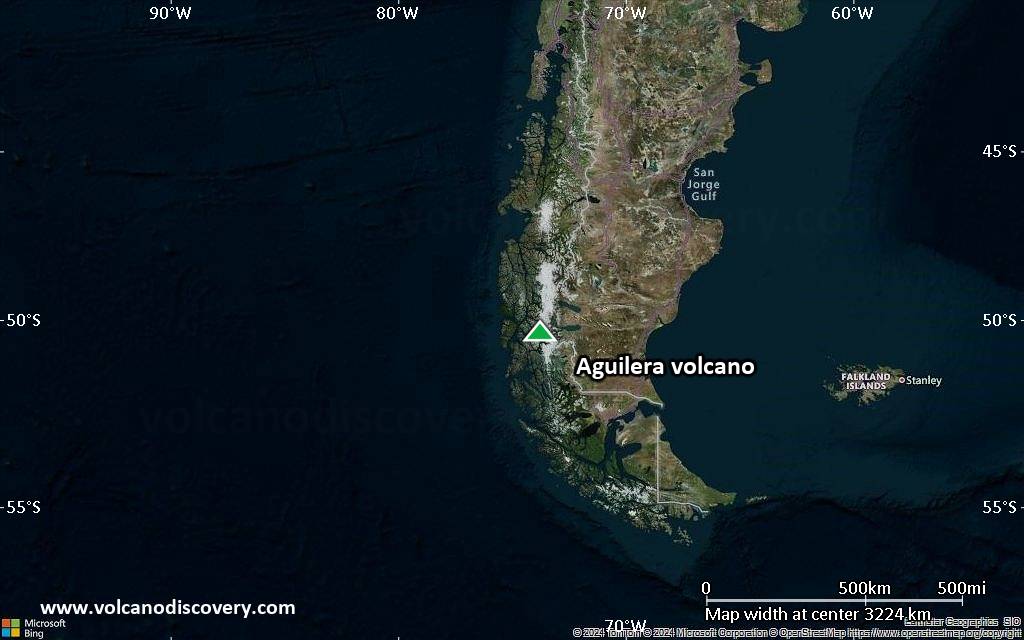
Satellite/aerial-type map of Aguilera volcano (region scale large)
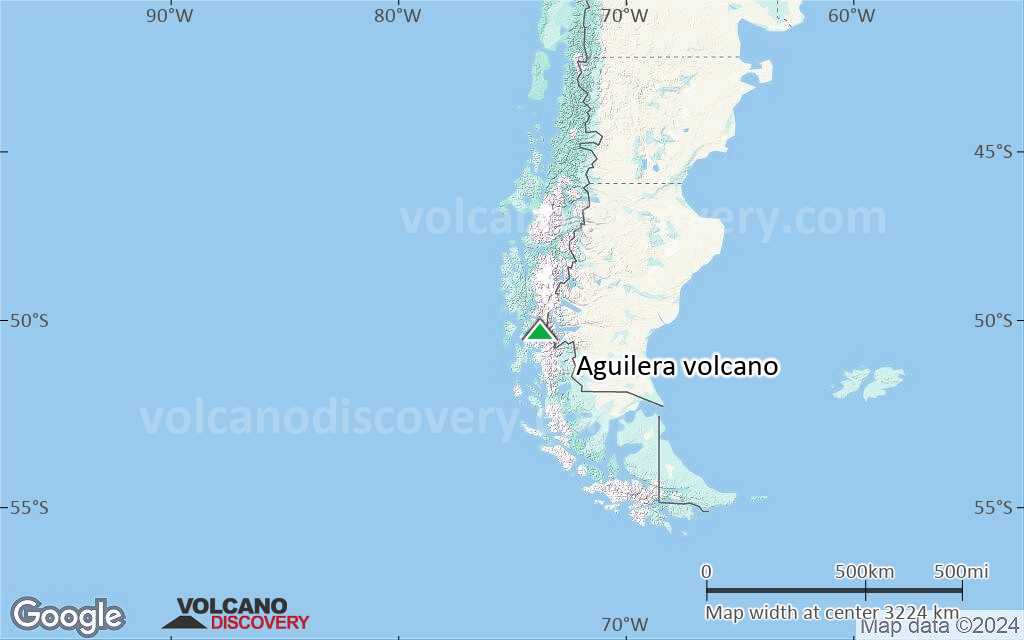
Terrain-type map of Aguilera volcano (region scale large)
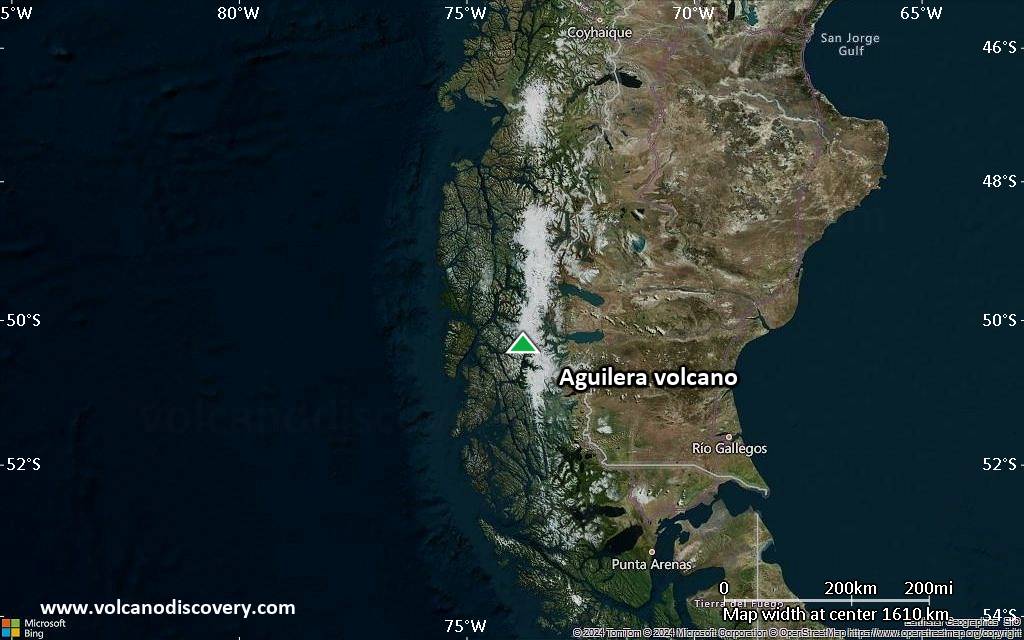
Satellite/aerial-type map of Aguilera volcano (region scale medium)

Terrain-type map of Aguilera volcano (region scale medium)
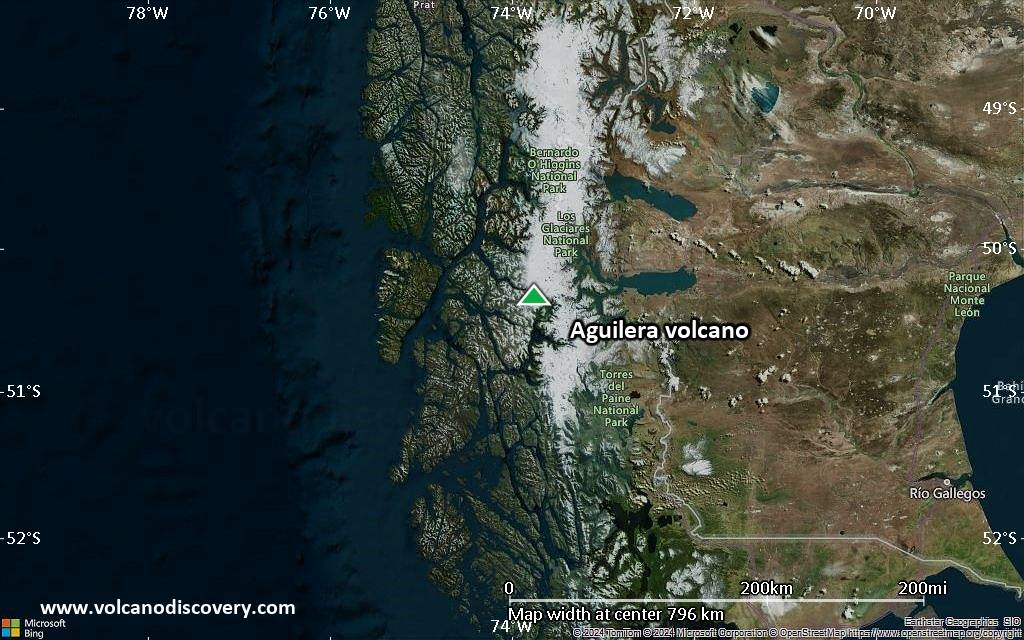
Satellite/aerial-type map of Aguilera volcano (region scale small)

Terrain-type map of Aguilera volcano (region scale small)
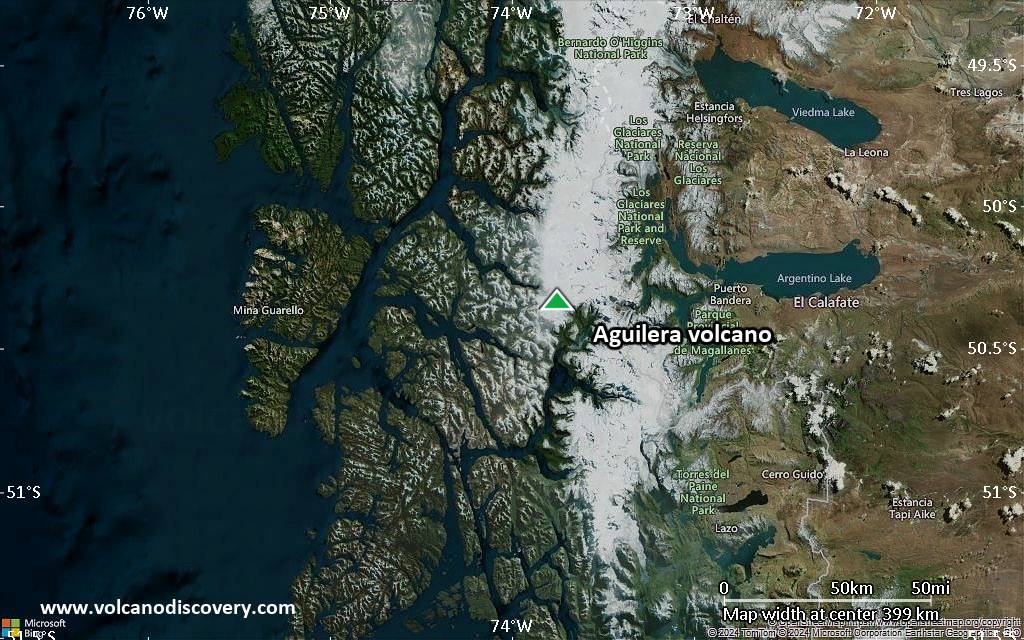
Satellite/aerial-type map of Aguilera volcano (local scale large)
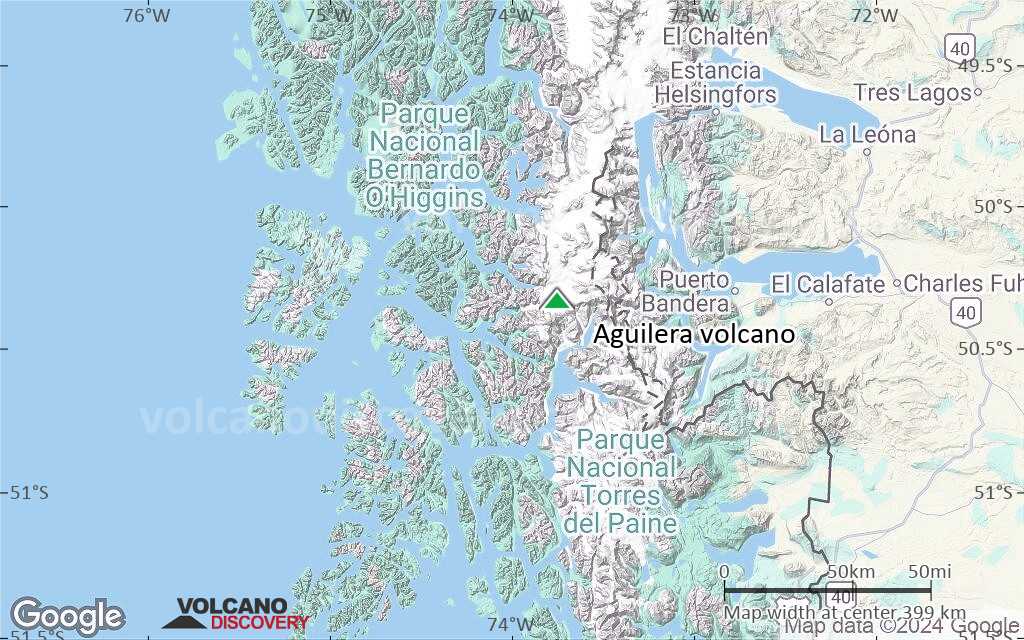
Terrain-type map of Aguilera volcano (local scale large)
Satellite/aerial-type map of Aguilera volcano (local scale medium)
Terrain-type map of Aguilera volcano (local scale medium)
Satellite/aerial-type map of Aguilera volcano (local scale small)
Terrain-type map of Aguilera volcano (local scale small)

Satellite/aerial-type map of Aguilera volcano (scale of 10s of km)
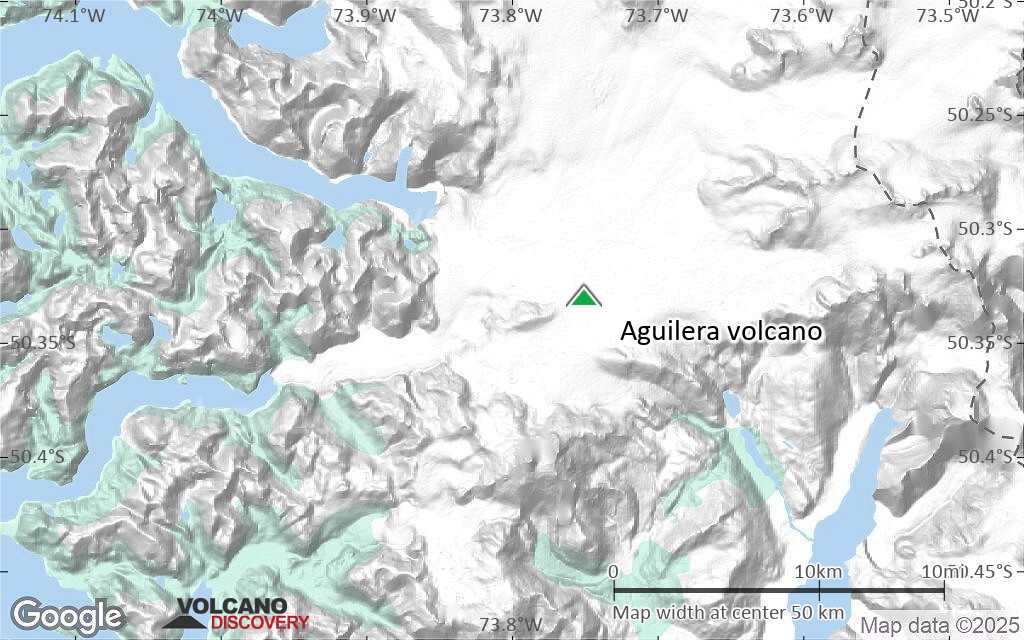
Terrain-type map of Aguilera volcano (scale of 10s of km)

Satellite/aerial-type map of Aguilera volcano (scale of 20-40 km)
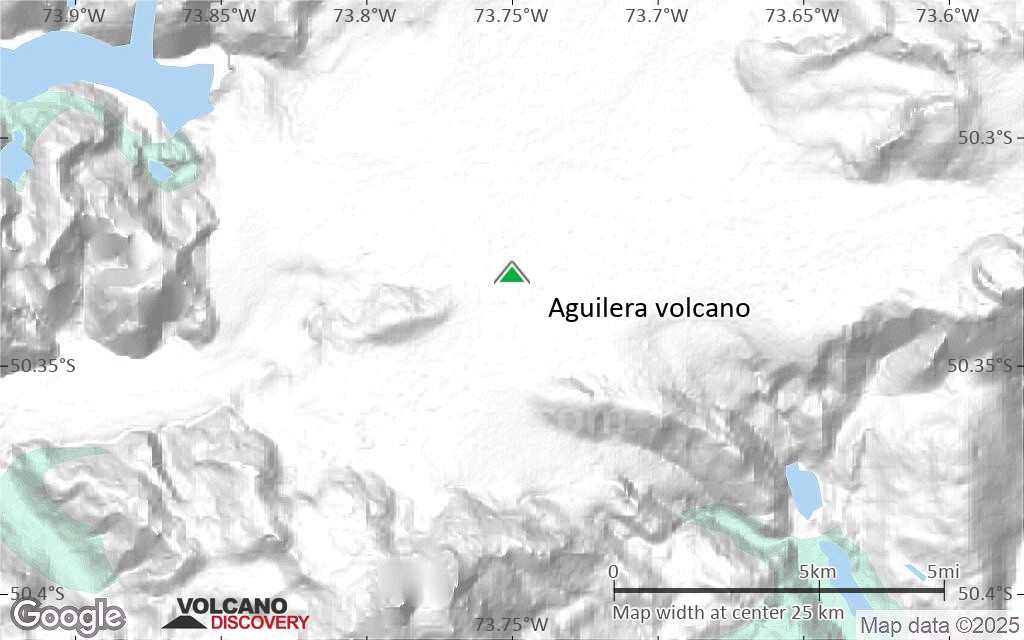
Terrain-type map of Aguilera volcano (scale of 20-40 km)

Satellite/aerial-type map of Aguilera volcano (scale of approx. 10-20 km)
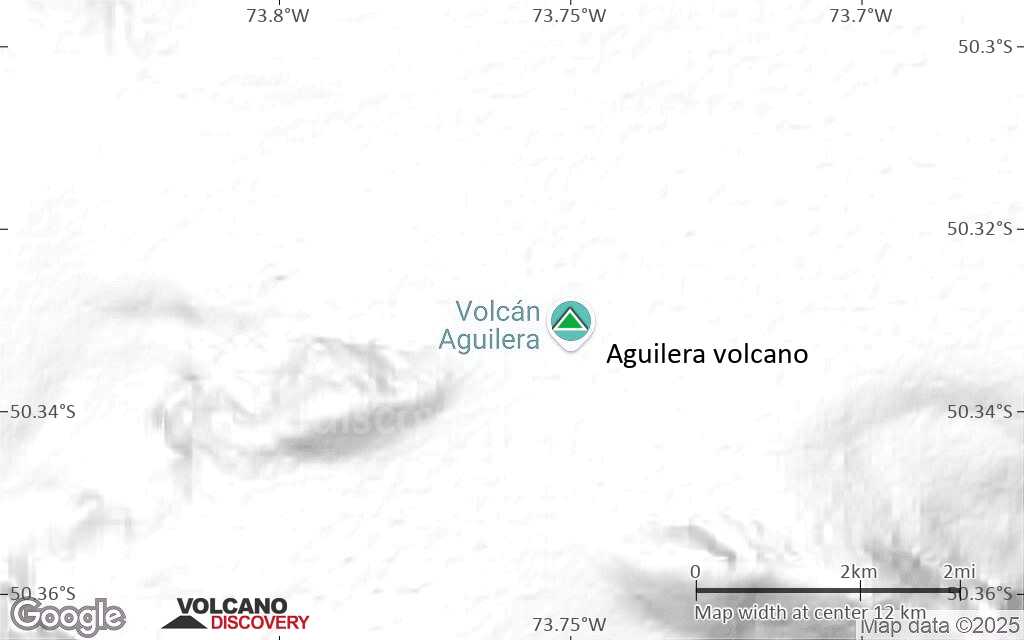
Terrain-type map of Aguilera volcano (scale of approx. 10-20 km)

Satellite/aerial-type map of Aguilera volcano (scale of 5-10 km)

Satellite/aerial-type map of Aguilera volcano (scale of few kilometers)





















