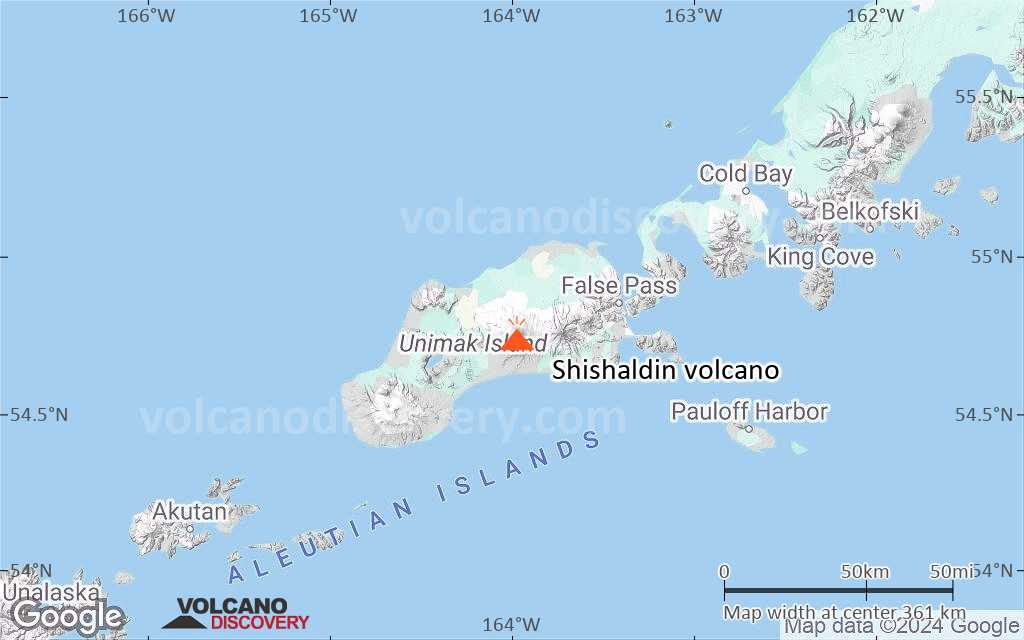
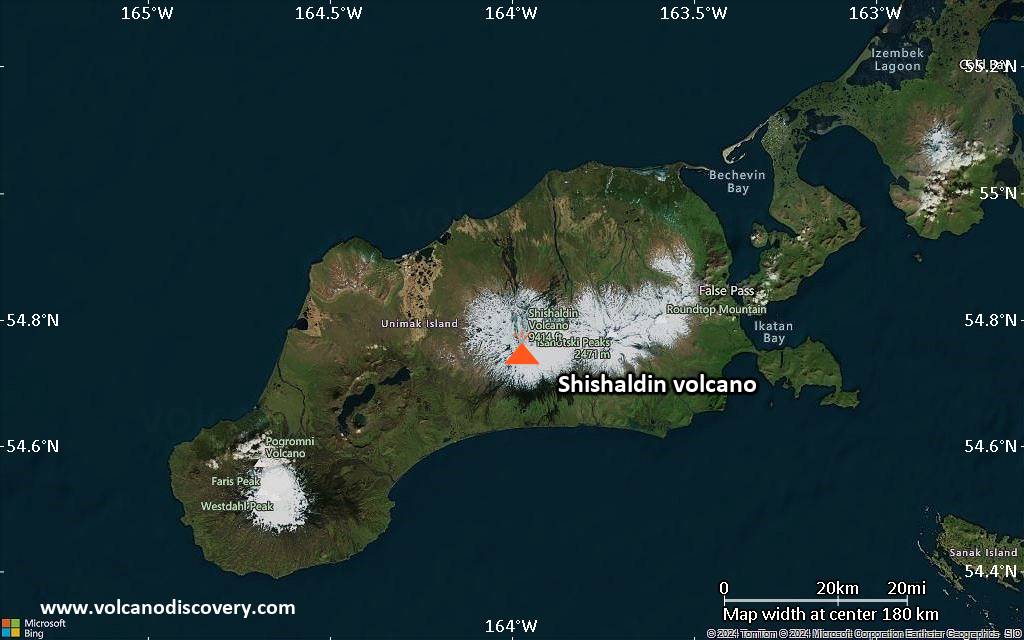
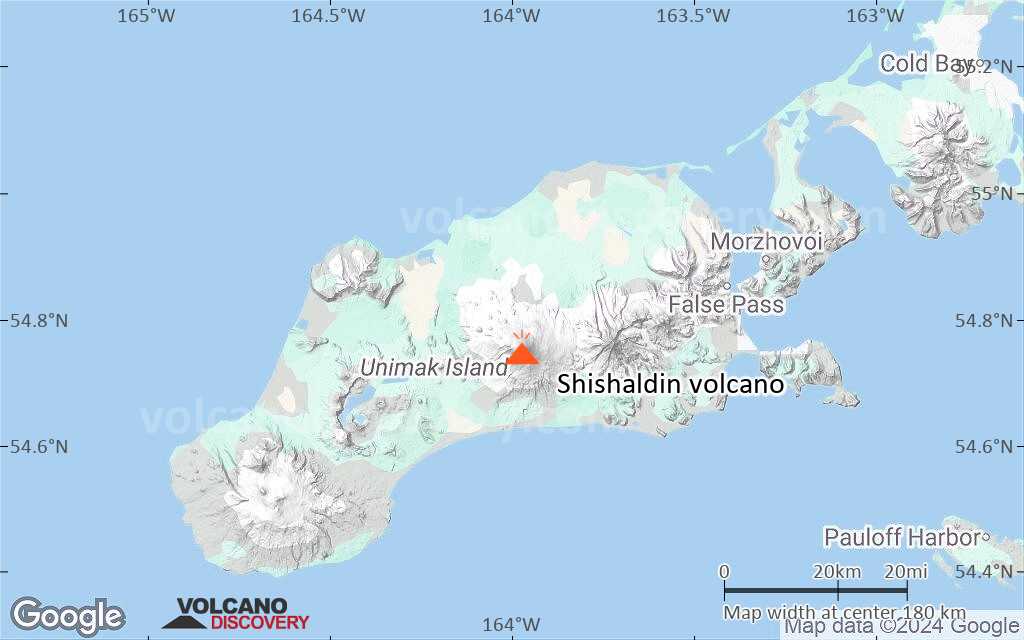
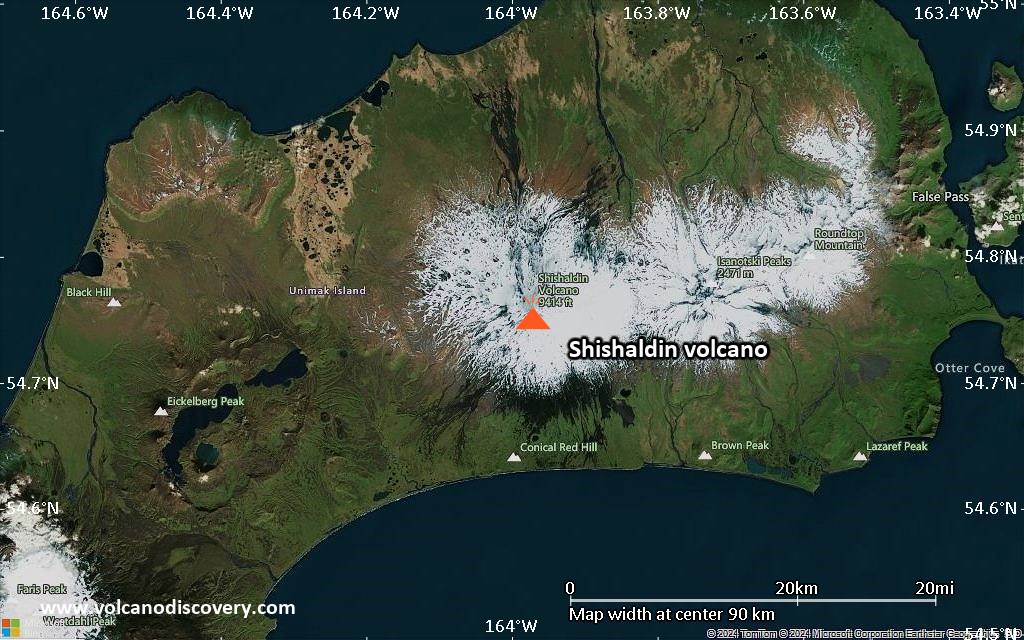
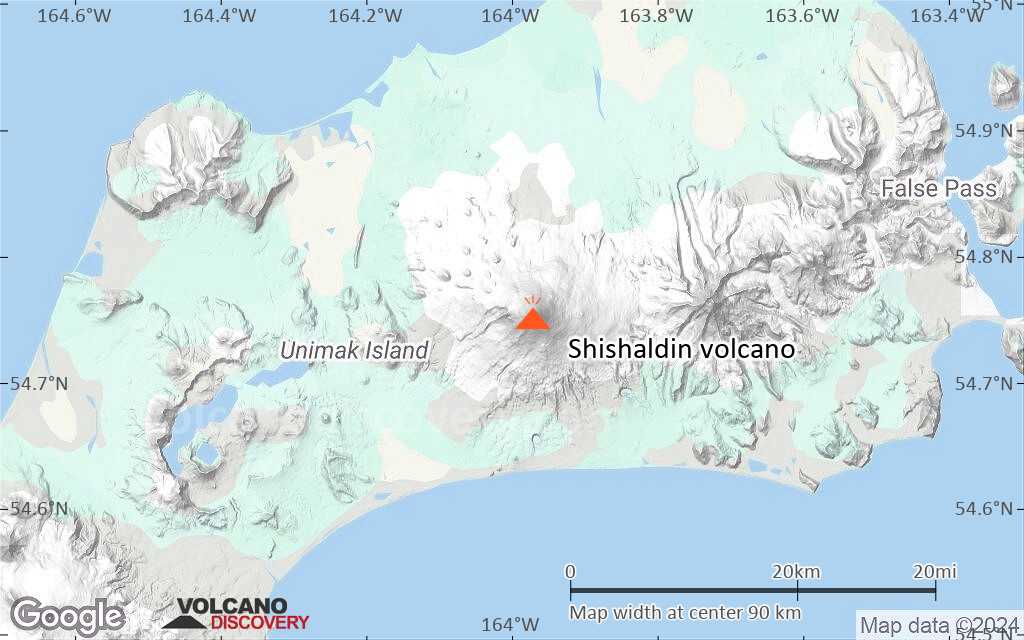
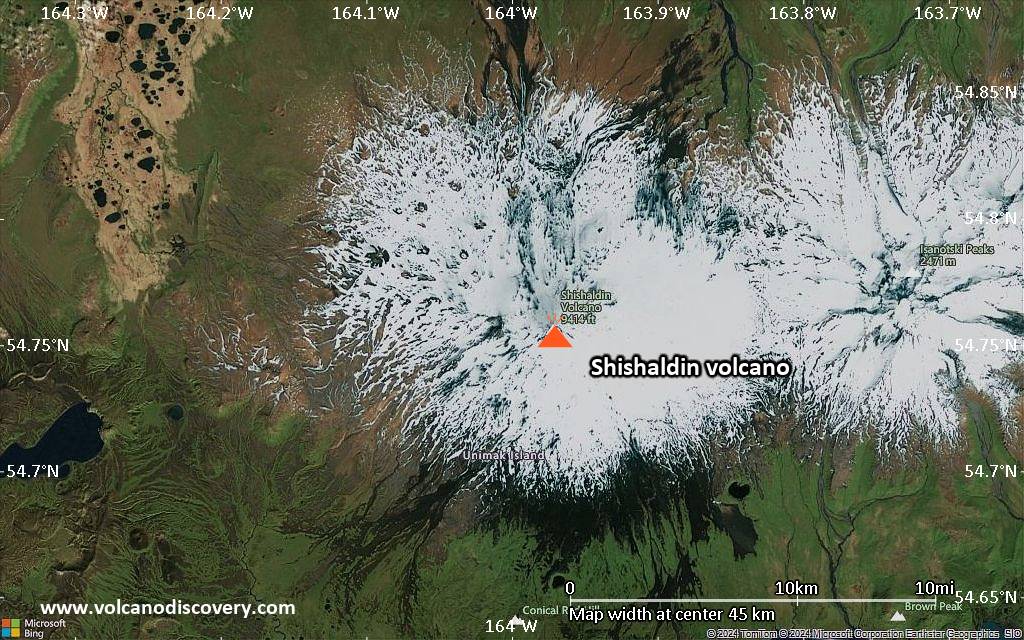
Shishaldin Volcano
Shishaldin volcano eruptions: 2023 (Jul 12-ongoing), 2019 (Jul 23 - 2020 May 4), 2014-15, 2008 (?), 2004, 2002, 2000, 1999, 1997, 1995, 1993, 1986-87, 1981 (?), 1979, 1978, 1976, 1975, 1967, 1963, 1955, 1953, 1951, 1948, 1946-47, 1932, 1929, 1928, 1927, 1925, 1922, 1912 (?), 1901, 1899 (?), 1898, 1897 (?), 1883, 1880-81, 1865 (?), 1842, 1838, 1830, 1927-29, 1826, 1825, 1824, 1790 (?), 1775-78
Latest nearby earthquakes
| Date and Time | Mag / Depth | Distance / Location | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oct 28, 12:07 pm (Universal Time) | 0.9 1.4 km | 1 km (0.6 mi) to the S | Info | ||
| Oct 28, 10:27 am (Universal Time) | 1.0 4.9 km | 1.8 km (1.1 mi) to the S | Info | ||
| Oct 28, 10:05 am (Universal Time) | 0.7 9.5 km | 3.1 km (1.9 mi) to the W | Info | ||
| Oct 28, 06:23 am (Universal Time) | 1.1 5 km | 2 km (1.2 mi) to the S | Info | ||
| Oct 28, 04:28 am (Universal Time) | 0.6 7.9 km | 2.3 km (1.4 mi) to the SW | Info | ||
| Oct 27, 04:25 pm (GMT -8) | 1.2 7 km | 1 km (0.6 mi) to the W | Info | ||
| Monday, October 27, 2025 GMT (1 quake) | |||||
| Oct 27, 05:12 pm (Universal Time) | 0.3 1.4 km | 1.7 km (1.1 mi) to the W | Info | ||
| Sunday, October 26, 2025 GMT (2 quakes) | |||||
| Oct 26, 11:28 pm (Universal Time) | 1.1 10.4 km | 2.2 km (1.4 mi) to the NE | Info | ||
| Oct 25, 04:36 pm (GMT -8) | 1.0 0.8 km | 18 km (10.9 mi) to the S | Info | ||
Background
The beautifully symmetrical volcano of Shishaldin is the highest and one of the most active volcanoes of the Aleutian Islands. The 2857-m-high, glacier-covered volcano is the westernmost of three large stratovolcanoes along an E-W line in the eastern half of Unimak Island. The Aleuts named the volcano Sisquk, meaning "mountain which points the way when I am lost." A steady steam plume rises from its small summit crater. Constructed atop an older glacially dissected volcano, Shishaldin is Holocene in age and largely basaltic in composition. Remnants of an older ancestral volcano are exposed on the west and NE sides at 1500-1800 m elevation. Shishaldin contains over two dozen pyroclastic cones on its NW flank, which is blanketed by massive aa lava flows. Frequent explosive activity, primarily consisting of strombolian ash eruptions from the small summit crater, but sometimes producing lava flows, has been recorded since the 18th century.---
Smithsonian / GVP volcano information
Shishaldin Volcano Photos




Significant volcanic eruptions: Shishaldin volcano
Additionally, there are 11 uncertain or discredited eruptions from Shishaldin volcano.
| Date | Note | VEI | Deaths | Damage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Historical obs./docs. | 3 | ||||
| Summit crater Historical obs./docs. | 3 | ||||
| Summit crater Historical obs./docs. | 1 | ||||
?? | Uncertain Eruption | 1? | |||
Historical obs./docs. | 2 | ||||
?? | Uncertain Eruption | 1? | |||
?? | Uncertain Eruption | 1? | |||
Historical obs./docs. | 3 | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | 1 | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | 1 | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | 3 | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | 2 | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | 2 | ||||
?? | Uncertain Eruption | ? | |||
Historical obs./docs. | 2 | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | 2 | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | 2 | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | 2 | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | 2 | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | 2 | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | 2 | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | 2 | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | 2 | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | 2 | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | 2 | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | 2 | ||||
| Summit and north flank Historical obs./docs. | 2 | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | 2 | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | ? | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | ? | ||||
Historical obs./docs. | 2 | ||||
?? | Uncertain Eruption | ? | |||
Historical obs./docs. | ? | ||||
Shishaldin Volcano FAQ
+When was the last eruption of Shishaldin volcano?
The last confirmed eruption of Shishaldin occurred in 2023.
+How often does Shishaldin volcano erupt?
Since 1824, Shishaldin volcano has had at least 37 historically documented eruptions. This means that it erupts on average every 5.4 years.
Many eruptions of Shishaldin have lasted more than one year. In total, the volcano has been in eruption during 45 out of 201 years until now. In other words, Shishaldin has been active at least one in 4.5 years on average. Note that this value is likely an underestimate, because the known history of eruptions from Shishaldin is likely incomplete, especially further back in time.
+How active is Shishaldin volcano at present?
Shishaldin volcano is very active: Since 1900, it has had 33 eruptions, and been active during 33 years out of 126 as of now. This means, Shishaldin has been in eruption one in 3.8 years on average. The last eruption was in 2023 and ended 2 years ago.
+When was the largest eruption of Shishaldin volcano?
The largest eruption of Shishaldin volcano in historic times occurred in 2023. It ranks as a "vulcanian" eruption with a magnitude 3 on the VEI (Volcanic Explosivity Index) scale.
Latest satellite images
Shishaldin Volcano Maps